SSD(Code-Model,Train & Test)
SSD 구현 (Model, Train & Test)
코드 참조: ChunML GitHub
위의 Code를 참조하여 수정한 SSD의 현재 Directory의 구조는 다음과 같습니다.(위의 Code는 SSD 300,512를 둘 다 구현하였지만, 현재 Code는 논문에서 예제로 보여준 SSD300을 고정으로서 사용하였습니다.)
Model
Model에 대한 전반적인 구조는 VGG16(Imagenet)으로서 Transfer Learning된 Model을 사용하여 구조를 형성하게 된다.
따라서 VGG16의 Network의 Architecture와 SSD가 어떻게 연결되는지 알아보면 다음과 같다.
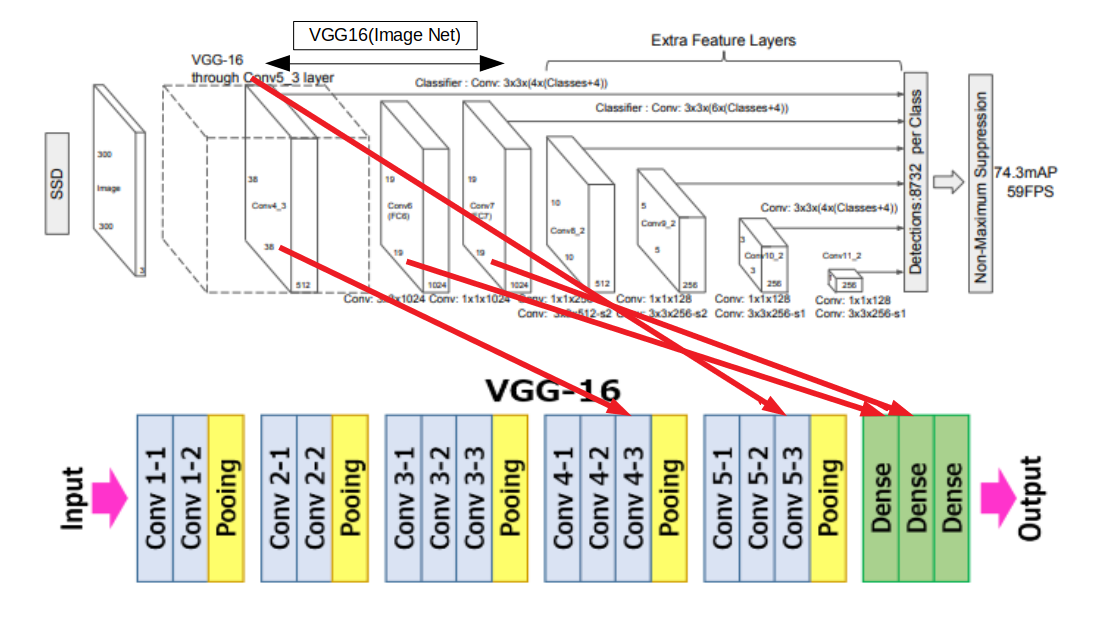
layer.py
기본적으로 Network를 구성하는 Layer들을 정의하는 곳 이다.
1) create_vgg16_layers()
- vgg16_conv4: PreTrainning된 VGG16 Model에서 Conv5_3 Layer까지 지정하는 곳 이다.
- vgg16_conv7: PreTrainning된 VGG16 Model에서 FcLayer6(Dense1), FcLaye7(Dense2)를 통과한 Layer를 지정하는 곳 이다.
2) create_extra_layers()
논문에서 다양한 Scale의 FeatureMap에서 ObjectDetection을 하기위한 Extra Feature Layers를 선언하는 곳 이다.
3) conf_head_layers()
Object의 Class를 확인하기 위한 Layer이다.
각각은 Default Box의 개수 * Class로서 Dimension을 이루고 논문과 같이 Convolution의 Filter의 Size는 3x3이다.
4) create_loc_head_layers()
Object의 Localization을 확인하기 위한 Layer이다.
각각은 Default Box의 개수 * (cx,cy,w,h) Dimension을 이루고 논문과 같이 Convolution의 Filter의 Size는 3x3이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow.keras.layers as layers
from tensorflow.keras import Sequential
def create_vgg16_layers():
vgg16_conv4 = [
layers.Conv2D(64, 3, padding='same', activation='relu'),
layers.Conv2D(64, 3, padding='same', activation='relu'),
layers.MaxPool2D(2, 2, padding='same'),
layers.Conv2D(128, 3, padding='same', activation='relu'),
layers.Conv2D(128, 3, padding='same', activation='relu'),
layers.MaxPool2D(2, 2, padding='same'),
layers.Conv2D(256, 3, padding='same', activation='relu'),
layers.Conv2D(256, 3, padding='same', activation='relu'),
layers.Conv2D(256, 3, padding='same', activation='relu'),
layers.MaxPool2D(2, 2, padding='same'),
layers.Conv2D(512, 3, padding='same', activation='relu'),
layers.Conv2D(512, 3, padding='same', activation='relu'),
layers.Conv2D(512, 3, padding='same', activation='relu'),
layers.MaxPool2D(2, 2, padding='same'),
layers.Conv2D(512, 3, padding='same', activation='relu'),
layers.Conv2D(512, 3, padding='same', activation='relu'),
layers.Conv2D(512, 3, padding='same', activation='relu'),
]
x = layers.Input(shape=[None, None, 3])
out = x
for layer in vgg16_conv4:
out = layer(out)
# PreTrainning된 VGG16 Model에서 Conv5_3 Layer까지 지정하는 곳 이다.
vgg16_conv4 = tf.keras.Model(x, out)
# PreTrainning된 VGG16 Model에서 FcLayer6(Dense1), FcLaye7(Dense2)를 통과한 Layer를 지정하는 곳 이다.
vgg16_conv7 = [
# Difference from original VGG16:
# 5th maxpool layer has kernel size = 3 and stride = 1
layers.MaxPool2D(3, 1, padding='same'),
# atrous conv2d for 6th block
layers.Conv2D(1024, 3, padding='same',
dilation_rate=6, activation='relu'),
layers.Conv2D(1024, 1, padding='same', activation='relu'),
]
x = layers.Input(shape=[None, None, 512])
out = x
for layer in vgg16_conv7:
out = layer(out)
vgg16_conv7 = tf.keras.Model(x, out)
return vgg16_conv4, vgg16_conv7
# 논문에서 다양한 Scale의 FeatureMap에서 ObjectDetection을 하기위한
# Extra Feature Layers를 선언하는 곳 이다.
def create_extra_layers():
""" Create extra layers
8th to 11th blocks
"""
extra_layers = [
# 8th block output shape: B, 512, 10, 10
Sequential([
layers.Conv2D(256, 1, activation='relu'),
layers.Conv2D(512, 3, strides=2, padding='same',
activation='relu'),
]),
# 9th block output shape: B, 256, 5, 5
Sequential([
layers.Conv2D(128, 1, activation='relu'),
layers.Conv2D(256, 3, strides=2, padding='same',
activation='relu'),
]),
# 10th block output shape: B, 256, 3, 3
Sequential([
layers.Conv2D(128, 1, activation='relu'),
layers.Conv2D(256, 3, activation='relu'),
]),
# 11th block output shape: B, 256, 1, 1
Sequential([
layers.Conv2D(128, 1, activation='relu'),
layers.Conv2D(256, 3, activation='relu'),
])
]
return extra_layers
# Object의 Class를 확인하기 위한 Layer이다.
# 각각은 Default Box의 개수 * Class로서 Dimension을 이루고
# 논문과 같이 Convolution의 Filter의 Size는 3x3이다.
def create_conf_head_layers(num_classes):
""" Create layers for classification
"""
conf_head_layers = [
layers.Conv2D(4 * num_classes, kernel_size=3,
padding='same'), # for 4th block
layers.Conv2D(6 * num_classes, kernel_size=3,
padding='same'), # for 7th block
layers.Conv2D(6 * num_classes, kernel_size=3,
padding='same'), # for 8th block
layers.Conv2D(6 * num_classes, kernel_size=3,
padding='same'), # for 9th block
layers.Conv2D(4 * num_classes, kernel_size=3,
padding='same'), # for 10th block
layers.Conv2D(4 * num_classes, kernel_size=3,
padding='same') # for 11th block
]
return conf_head_layers
# Object의 Localization을 확인하기 위한 Layer이다.
# 각각은 Default Box의 개수 * (cx,cy,w,h) Dimension을 이루고
# 논문과 같이 Convolution의 Filter의 Size는 3x3이다.
def create_loc_head_layers():
""" Create layers for regression
"""
loc_head_layers = [
layers.Conv2D(4 * 4, kernel_size=3, padding='same'),
layers.Conv2D(6 * 4, kernel_size=3, padding='same'),
layers.Conv2D(6 * 4, kernel_size=3, padding='same'),
layers.Conv2D(6 * 4, kernel_size=3, padding='same'),
layers.Conv2D(4 * 4, kernel_size=3, padding='same'),
layers.Conv2D(4 * 4, kernel_size=3, padding='same')
]
return loc_head_layers
network.py
위에서 선언한 Layers.py를 통하여 SSD Network를 구성한다.
기본적으로 layers.py에서 다 선언한 것을 이어주는 것이 대부분이다.
조금 중요하게 살펴보아야 할 부분을 살펴보면 다음과 같다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
fc1_weights, fc1_biases = origin_vgg.get_layer(index=-3).get_weights()
fc2_weights, fc2_biases = origin_vgg.get_layer(index=-2).get_weights()
conv6_weights = np.random.choice(np.reshape(fc1_weights, (-1,)), (3, 3, 512, 1024))
conv6_biases = np.random.choice(fc1_biases, (1024,))
conv7_weights = np.random.choice(np.reshape(fc2_weights, (-1,)), (1, 1, 1024, 1024))
conv7_biases = np.random.choice(fc2_biases, (1024,))
self.vgg16_conv7.get_layer(index=2).set_weights([conv6_weights, conv6_biases])
self.vgg16_conv7.get_layer(index=3).set_weights([conv7_weights, conv7_biases])
VGG16의 마지막 단을 살펴보면 FC6 -> FC7 -> Softmax로서 Classify를 한다.
따라서 PreTraining된 VGG16 Model에서 마지막에서 3번째를 FC6 -> conv6, FC7 -> conv7로서 선언하는 것이 중요한다.
1
2
3
4
for i in range(len(self.vgg16_conv4.layers)):
x = self.vgg16_conv4.get_layer(index=i)(x)
if i == len(self.vgg16_conv4.layers) - 5:
conf, loc = self.compute_heads(self.batch_norm(x), head_idx)
논문에서 살펴보면 VGG16의 모델을 Conv5_3 Layer까지 사용하나 마지막에 Detection을 하는 부분은 Conv4_3 Layer에서 가져온다.
따라서 위와 같은 과정을 거쳐서 FeatureMap을 생성해야 한다.
최종적인 결과로서 모든 FeaturMap을 하나로 연결(confs, locs)하여 Network의 Output이 생성된다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
from tensorflow.keras import Model
from tensorflow.keras.applications import VGG16
import tensorflow.keras.layers as layers
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import os
from layers import create_vgg16_layers, create_extra_layers, create_conf_head_layers, create_loc_head_layers
class SSD(Model):
""" Class for SSD model
Attributes:
num_classes: number of classes
"""
def __init__(self, num_classes):
super(SSD, self).__init__()
self.arch = 'ssd300'
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.vgg16_conv4, self.vgg16_conv7 = create_vgg16_layers()
self.batch_norm = layers.BatchNormalization(
beta_initializer='glorot_uniform',
gamma_initializer='glorot_uniform'
)
self.extra_layers = creatcompute_headse_extra_layers()
self.conf_head_layers = create_conf_head_layers(num_classes)
self.loc_head_layers = create_loc_head_layers()
def compute_heads(self, x, idx):
""" Compute outputs of classification and regression heads
Args:
x: the input feature map
idx: index of the head layer
Returns:
conf: output of the idx-th classification head
loc: output of the idx-th regression head
"""
conf = self.conf_head_layers[idx](x)
conf = tf.reshape(conf, [conf.shape[0], -1, self.num_classes])
loc = self.loc_head_layers[idx](x)
loc = tf.reshape(loc, [loc.shape[0], -1, 4])
return conf, loc
def init_vgg16(self):
""" Initialize the VGG16 layers from pretrained weights
and the rest from scratch using xavier initializer
"""
origin_vgg = VGG16(weights='imagenet')
for i in range(len(self.vgg16_conv4.layers)):
self.vgg16_conv4.get_layer(index=i).set_weights(
origin_vgg.get_layer(index=i).get_weights())
fc1_weights, fc1_biases = origin_vgg.get_layer(index=-3).get_weights()
fc2_weights, fc2_biases = origin_vgg.get_layer(index=-2).get_weights()
conv6_weights = np.random.choice(
np.reshape(fc1_weights, (-1,)), (3, 3, 512, 1024))
conv6_biases = np.random.choice(
fc1_biases, (1024,))
conv7_weights = np.random.choice(
np.reshape(fc2_weights, (-1,)), (1, 1, 1024, 1024))
conv7_biases = np.random.choice(
fc2_biases, (1024,))
self.vgg16_conv7.get_layer(index=2).set_weights(
[conv6_weights, conv6_biases])
self.vgg16_conv7.get_layer(index=3).set_weights(
[conv7_weights, conv7_biases])
def call(self, x):
""" The forward pass
Args:
x: the input image
Returns:
confs: list of outputs of all classification heads
locs: list of outputs of all regression heads
"""
confs = []
locs = []
head_idx = 0
for i in range(len(self.vgg16_conv4.layers)):
x = self.vgg16_conv4.get_layer(index=i)(x)
if i == len(self.vgg16_conv4.layers) - 5:
conf, loc = self.compute_heads(self.batch_norm(x), head_idx)
confs.append(conf)
locs.append(loc)
head_idx += 1
x = self.vgg16_conv7(x)
conf, loc = self.compute_heads(x, head_idx)
confs.append(conf)
locs.append(loc)
head_idx += 1
for layer in self.extra_layers:
x = layer(x)
conf, loc = self.compute_heads(x, head_idx)
confs.append(conf)
locs.append(loc)
head_idx += 1
confs = tf.concat(confs, axis=1)
locs = tf.concat(locs, axis=1)
return confs, locs
def create_ssd(num_classes, pretrained_type,
checkpoint_dir=None,
checkpoint_path=None):
""" Create SSD model and load pretrained weights
Args:
num_classes: number of classes
pretrained_type: type of pretrained weights, can be either 'VGG16' or 'ssd'
weight_path: path to pretrained weights
Returns:
net: the SSD model
"""
net = SSD(num_classes)
net(tf.random.normal((1, 512, 512, 3)))
if pretrained_type == 'base':
net.init_vgg16()
elif pretrained_type == 'latest':
try:
paths = [os.path.join(checkpoint_dir, path)
for path in os.listdir(checkpoint_dir)]
latest = sorted(paths, key=os.path.getmtime)[-1]
net.load_weights(latest)
except AttributeError as e:
print('Please make sure there is at least one checkpoint at {}'.format(
checkpoint_dir))
print('The model will be loaded from base weights.')
net.init_vgg16()
except Exception as e:
print(e)
raise ValueError('Please check if checkpoint_dir is specified')
elif pretrained_type == 'specified':
if not os.path.isfile(checkpoint_path):
raise ValueError(
'Not a valid checkpoint file: {}'.format(checkpoint_path))
try:
net.load_weights(checkpoint_path)
except Exception as e:
raise ValueError(
'Please check the following\n1./ Is the path correct: {}?\n2./ Is the model architecture correct: {}?'.format(
checkpoint_path, 'ssd300'))
else:
raise ValueError('Unknown pretrained type: {}'.format(pretrained_type))
return net
loss.py
최종적인 SSD Model의 Loss를 구하는 방법이다.
hard_negative_mining()
논문에서는 Image의 Pixel에서 Default Box가 Background인 것이 많아서 LossFunction에서 Positive:Negative의 비율을 High confidence기준으로 1:3으로서 뽑게 하였다.
따라서 Loss기준으로 Highconfidence로서 정렬하고 num_neg = num_pos * neg_ratio(=3)으로서 정의하였다.
class SSDLosses()
실제 최종적인 Loss를 구하는 방법이다.
Localization Loss
$$L_{loc}(x,l,g) = \sum_{i \in Pos}^N \sum_{m \in cx,cy,w,h} x_{ij}^k smooth_{L1}(l_i^m-\hat{g}_j^m)$$
$$\hat{g}_j^{cx}=(g_j^{cx}-d_i^{cx})/d_i^w, \hat{g}_j^{cy}=(g_j^{cy}-d_i^{cy})/d_i^h$$
$$\hat{g}_j^{w} = log(\frac{g_j^w}{d_i^w}), \hat{g}_j^{h} = log(\frac{g_j^h}{d_i^h})$$
$$ x_{ij}^p= \begin{cases} 1, & \mbox{if } IOU > 0.5 \mbox{ between default box i and ground true box j on class p} \\ 0, & \mbox{otherwise} \end{cases} $$
실제 Code에서도 SmoothL1(smooth_l1_loss = tf.keras.losses.Huber(reduction='sum'))로서 구현
Confidence Loss
$$L_{conf}(x,c) = -\sum_{i \in Pos}^N x_{ij}^p log(\hat{c}_i^p)-\sum_{i \in Neg} log(\hat{c}_i^0) \text{, where } \hat{c}_i^p = \frac{exp(c_i^p)}{\sum_p c_i^p}$$
COnfidence loss에서 중요한 점은 0(Background)의 값이 높기 때문에 hard_negative_mining를 적용시킨다.
실제 Code에서도 CrossEntropy(cross_entropy = tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True, reduction='sum'))로서 구현
Final Loss
$$L(x,c,l,g) = \frac{1}{N}(L_{conf}(x,c) + \alpha L_{loc}(x,l,g))$$
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
import tensorflow as tf
def hard_negative_mining(loss, gt_confs, neg_ratio=3):
""" Hard negative mining algorithm
to pick up negative examples for back-propagation
base on classification loss values
Args:
loss: list of classification losses of all default boxes (B, num_default)
gt_confs: classification targets (B, num_default)
neg_ratio: negative / positive ratio
Returns:
conf_loss: classification loss
loc_loss: regression loss
"""
# loss: B x N
# gt_confs: B x N
pos_idx = gt_confs > 0
num_pos = tf.reduce_sum(tf.dtypes.cast(pos_idx, tf.int32), axis=1)
num_neg = num_pos * neg_ratio
rank = tf.argsort(loss, axis=1, direction='DESCENDING')
rank = tf.argsort(rank, axis=1)
neg_idx = rank < tf.expand_dims(num_neg, 1)
return pos_idx, neg_idx
class SSDLosses(object):
""" Class for SSD Losses
Attributes:
neg_ratio: negative / positive ratio
num_classes: number of classes
"""
def __init__(self, neg_ratio, num_classes):
self.neg_ratio = neg_ratio
self.num_classes = num_classes
def __call__(self, confs, locs, gt_confs, gt_locs):
""" Compute losses for SSD
regression loss: smooth L1
classification loss: cross entropy
Args:
confs: outputs of classification heads (B, num_default, num_classes)
locs: outputs of regression heads (B, num_default, 4)
gt_confs: classification targets (B, num_default)
gt_locs: regression targets (B, num_default, 4)
Returns:
conf_loss: classification loss
loc_loss: regression loss
"""
cross_entropy = tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(
from_logits=True, reduction='none')
# compute classification losses
# without reduction
temp_loss = cross_entropy(
gt_confs, confs)
pos_idx, neg_idx = hard_negative_mining(
temp_loss, gt_confs, self.neg_ratio)
# classification loss will consist of positive and negative examples
cross_entropy = tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(
from_logits=True, reduction='sum')
smooth_l1_loss = tf.keras.losses.Huber(reduction='sum')
conf_loss = cross_entropy(
gt_confs[tf.math.logical_or(pos_idx, neg_idx)],
confs[tf.math.logical_or(pos_idx, neg_idx)])
# regression loss only consist of positive examples
loc_loss = smooth_l1_loss(
# tf.boolean_mask(gt_locs, pos_idx),
# tf.boolean_mask(locs, pos_idx))
gt_locs[pos_idx],
locs[pos_idx])
num_pos = tf.reduce_sum(tf.dtypes.cast(pos_idx, tf.float32))
conf_loss = conf_loss / num_pos
loc_loss = loc_loss / num_pos
return conf_loss, loc_loss
def create_losses(neg_ratio, num_classes):
criterion = SSDLosses(neg_ratio, num_classes)
return criterion
Train & Test
train.py
위에서 설명하였던 Utils,Dataset,Model을 활용하여 실제 SSD Model을 Trainning하는 방법이다.
아래와 같은 Code로서 실행 가능하고 다양한 Option은 바꿔서 실행가능하다.
train.py 실행 에시
python train.py --batch-size 4 --gpu-id 0
train.py Option List
usage: train.py [-h] [--data-dir DATA_DIR] [--batch-size BATCH_SIZE]
[--num-batches NUM_BATCHES] [--neg-ratio NEG_RATIO]
[--initial-lr INITIAL_LR] [--momentum MOMENTUM]
[--weight-decay WEIGHT_DECAY] [--num-epochs NUM_EPOCHS]
[--checkpoint-dir CHECKPOINT_DIR]
train_step()
실제 LossFunction을 계산하고 Backpropagation을 진행하는 곳 이다.
Paper와 동일하게 다음과 같이 Hyperparameter를 선언하였다.
We fine-tune the resulting model using SGD with initial learning rate 10−3 , 0.9 momentum, 0.0005 weight decay, and batch size 32.
The learning rate decay policy is slightly different for each dataset, and we will describe details later
- learning rate(
parser.add_argument('--initial-lr', default=1e-3, type=float)): 10-3 - momentum(
parser.add_argument('--momentum', default=0.9, type=float)): 0.9 - weight decay(
parser.add_argument('--weight-decay', default=5e-4, type=float)): 0.0005 - batch size(
parser.add_argument('--batch-size', default=32, type=int)): 32 NUM_CLASSES = 21: # 20개의 Class + 1개의 Background
나머지의 사항은 기본적으로 해왔던 Model을 Training하는 과정과 같다.
자세한 사항은 Code에 주석으로서 첨부하였다.
참고사항(batch-size)
현재 Local Notebook에서는 Batch Size 32는 Training되지 않아서 Batch Size를 4로서 현저히 줄인뒤 Training하였다.
참고사항(PiecewiseConstantDecay)
논문에서 재시한 Learning Rate를 변경하는 방법이다.
현재 Code는 tensorflow.keras.optimizers.schedules.PiecewiseConstantDecay를 활용하여 Learning Rate를 서서히 낮추는 방법을 사용하였다.
Applies exponential decay to the learning rate.
When training a model, it is often recommended to lower the learning rate as the training progresses. This schedule applies an exponential decay function to an optimizer step, given a provided initial learning rate.
__init__(
initial_learning_rate,
decay_steps,
decay_rate,
staircase=False,
name=None
)
참조: PiecewiseConstantDecay 사용법
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
import argparse
import tensorflow as tf
import os
import sys
import time
import yaml
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers.schedules import PiecewiseConstantDecay
from voc_data import create_batch_generator
from anchor import generate_default_boxes
from network import create_ssd
from losses import create_losses
# Paper와 같이 Hyperparameter를 Default로서 설정하였다.
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--batch-size', default=32, type=int)
parser.add_argument('--num-batches', default=-1, type=int)
parser.add_argument('--neg-ratio', default=3, type=int)
parser.add_argument('--initial-lr', default=1e-3, type=float)
parser.add_argument('--momentum', default=0.9, type=float)
parser.add_argument('--weight-decay', default=5e-4, type=float)
parser.add_argument('--num-epochs', default=120, type=int)
parser.add_argument('--checkpoint-dir', default='checkpoints')
parser.add_argument('--pretrained-type', default='base')
parser.add_argument('--gpu-id', default='0')
args = parser.parse_args()
# 사용가능한 GPU Device를 설정한다.
os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = args.gpu_id
# 20개의 Class + 1개의 Background
NUM_CLASSES = 21
# LossFunction과 Backpropagation을 징행한다.
@tf.function
def train_step(imgs, gt_confs, gt_locs, ssd, criterion, optimizer):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
confs, locs = ssd(imgs)
conf_loss, loc_loss = criterion(
confs, locs, gt_confs, gt_locs)
loss = conf_loss + loc_loss
# l2_loss = [tf.nn.l2_loss(t) for t in ssd.trainable_variables]
# l2_loss = args.weight_decay * tf.math.reduce_sum(l2_loss)
# loss += l2_loss
gradients = tape.gradient(loss, ssd.trainable_variables)
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients, ssd.trainable_variables))
return loss, conf_loss, loc_loss
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Model의 Checkpoints를 저장할 Directory가 없을 경우 생성한다.
os.makedirs(args.checkpoint_dir, exist_ok=True)
# 실제 SSD 300에 미리 저장되어 있는 Setting값을 가져와서 적용한다.(Anchor, FeatureMapSize 등)
with open('./config.yml') as f:
cfg = yaml.load(f, Loader=yaml.FullLoader)
config = cfg['SSD300']
default_boxes = generate_default_boxes(config)
# voc_data.py에서 설정한 Dataset을 Batch형태로서 가져온다.
batch_generator, val_generator, info = create_batch_generator(default_boxes,
args.batch_size, args.num_batches,
mode='train')
# 실제 SSD Model을 설정한다. 만약, Training중이던 Model이 있으면 그대로 가져가서 사용할 수 있다.
try:
ssd = create_ssd(NUM_CLASSES,
args.pretrained_type,
checkpoint_dir=args.checkpoint_dir)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
print('The program is exiting...')
sys.exit()
# Hard negative mining을 적용하여 Loss를 구한다.
criterion = create_losses(args.neg_ratio, NUM_CLASSES)
steps_per_epoch = info['length'] // args.batch_size
# 해당 논문에서는 The learning rate decay policy is slightly different for each dataset
# 로서 설명하였다. 정확한 방법은 나와있지 않아서 아마 원본 Code를 참고하여 만든 것 같다.
lr_fn = PiecewiseConstantDecay(
boundaries=[int(steps_per_epoch * args.num_epochs * 2 / 3),
int(steps_per_epoch * args.num_epochs * 5 / 6)],
values=[args.initial_lr, args.initial_lr * 0.1, args.initial_lr * 0.01])
# Optimizer 선언
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(
learning_rate=lr_fn,
momentum=args.momentum)
# Training의 과정을 저장할 tf.summary를 선언한다.
train_log_dir = 'logs/train'
val_log_dir = 'logs/val'
train_summary_writer = tf.summary.create_file_writer(train_log_dir)
val_summary_writer = tf.summary.create_file_writer(val_log_dir)
# 지정한 Epoch 만큼 Model을 Training한다.
for epoch in range(args.num_epochs):
avg_loss = 0.0
avg_conf_loss = 0.0
avg_loc_loss = 0.0
start = time.time()
for i, (_, imgs, gt_confs, gt_locs) in enumerate(batch_generator):
loss, conf_loss, loc_loss = train_step(
imgs, gt_confs, gt_locs, ssd, criterion, optimizer)
avg_loss = (avg_loss * i + loss.numpy()) / (i + 1)
avg_conf_loss = (avg_conf_loss * i + conf_loss.numpy()) / (i + 1)
avg_loc_loss = (avg_loc_loss * i + loc_loss.numpy()) / (i + 1)
# print(i)
# Batch 도중에 Loss를 확인한다.
if (i + 1) % 50 == 0:
print('Epoch: {} Batch {} Time: {:.2}s | Loss: {:.4f} Conf: {:.4f} Loc: {:.4f}'.format(
epoch + 1, i + 1, time.time() - start, avg_loss, avg_conf_loss, avg_loc_loss))
avg_val_loss = 0.0
avg_val_conf_loss = 0.0
avg_val_loc_loss = 0.0
# Training Data가 아닌 Validation으로서 확인한다.
for i, (_, imgs, gt_confs, gt_locs) in enumerate(val_generator):
val_confs, val_locs = ssd(imgs)
val_conf_loss, val_loc_loss = criterion(
val_confs, val_locs, gt_confs, gt_locs)
val_loss = val_conf_loss + val_loc_loss
avg_val_loss = (avg_val_loss * i + val_loss.numpy()) / (i + 1)
avg_val_conf_loss = (avg_val_conf_loss * i + val_conf_loss.numpy()) / (i + 1)
avg_val_loc_loss = (avg_val_loc_loss * i + val_loc_loss.numpy()) / (i + 1)
# Training Loss에 관하여 tf.summary를 이용하여 저장
with train_summary_writer.as_default():
tf.summary.scalar('loss', avg_loss, step=epoch)
tf.summary.scalar('conf_loss', avg_conf_loss, step=epoch)
tf.summary.scalar('loc_loss', avg_loc_loss, step=epoch)
# Validation Loss에 관하여 tf.summary를 이용하여 저장
with val_summary_writer.as_default():
tf.summary.scalar('loss', avg_val_loss, step=epoch)
tf.summary.scalar('conf_loss', avg_val_conf_loss, step=epoch)
tf.summary.scalar('loc_loss', avg_val_loc_loss, step=epoch)
# 일정 Epoch마다 Model을 Keras의 .h5형태로서 저장
if (epoch + 1) % 10 == 0:
ssd.save_weights(
os.path.join(args.checkpoint_dir, 'ssd_epoch_{}.h5'.format(epoch + 1)))
test.py
실제 Test Image로서 만들어진 Model의 결과를 확인하는 방법이다.
기본적으로 train.py와 구조가 같지만 실제 Image에 Detection한 결과를 겹치게 Image로서 저장하고 또한, 해당 Label을 저장하여 결과를 나타내게 된다.
실행 예시는 다음과 같다.
test.py 실행 에시
python test.py --checkpoint-path ./checkpoints/ssd_epoch_110.h5 --num-examples 40
test.py Option List
usage: test.py [-h] [--data-dir DATA_DIR] [--num-examples NUM_EXAMPLES]
[--pretrained-type PRETRAINED_TYPE]
[--checkpoint-dir CHECKPOINT_DIR]
[--checkpoint-path CHECKPOINT_PATH] [--gpu-id GPU_ID]
실형 결과
최종적인 실행 결과를 살펴보면 다음과 같다.
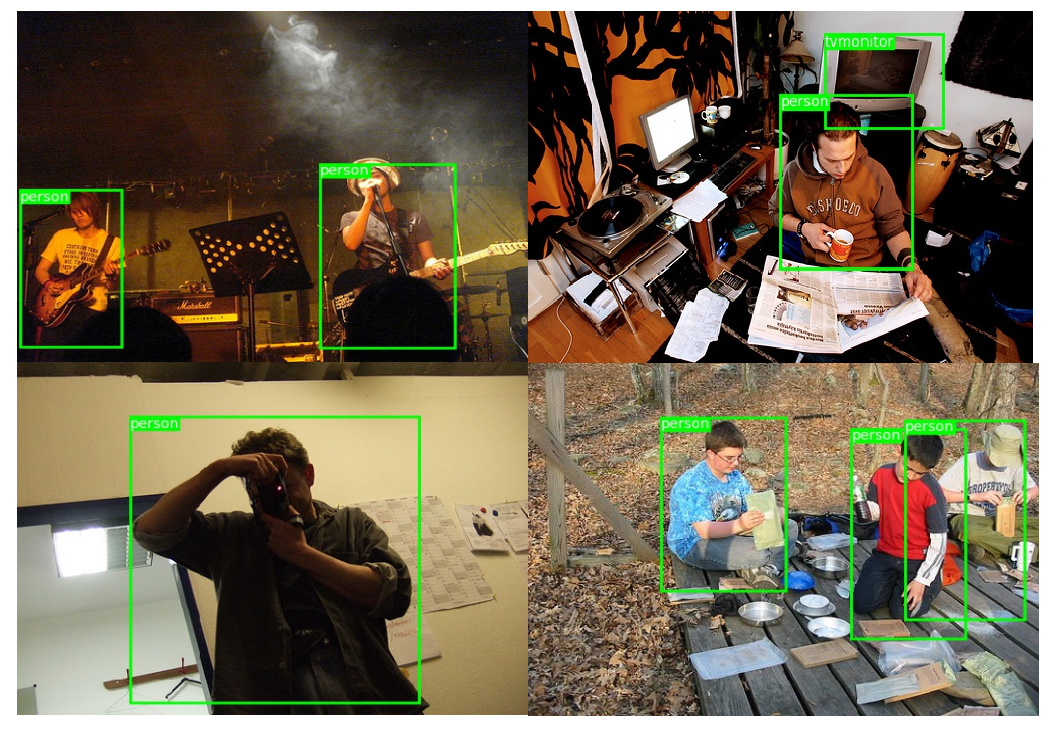

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
import argparse
import tensorflow as tf
import os
import sys
import numpy as np
import yaml
from tqdm import tqdm
from anchor import generate_default_boxes
from box_utils import decode, compute_nms
from voc_data import create_batch_generator
from image_utils import ImageVisualizer
from losses import create_losses
from network import create_ssd
from PIL import Image
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--data-dir', default='./data/preprocessing_test')
parser.add_argument('--num-examples', default=-1, type=int)
parser.add_argument('--pretrained-type', default='specified')
parser.add_argument('--checkpoint-dir', default='')
parser.add_argument('--checkpoint-path', default='')
parser.add_argument('--gpu-id', default='0')
args = parser.parse_args()
os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = args.gpu_id
NUM_CLASSES = 21
BATCH_SIZE = 1
# 실제 Image를 넣고 Object의 Localization과 Label의 Prediction한다.
def predict(imgs, default_boxes):
confs, locs = ssd(imgs)
confs = tf.squeeze(confs, 0)
locs = tf.squeeze(locs, 0)
confs = tf.math.softmax(confs, axis=-1)
classes = tf.math.argmax(confs, axis=-1)
scores = tf.math.reduce_max(confs, axis=-1)
boxes = decode(default_boxes, locs)
out_boxes = []
out_labels = []
out_scores = []
for c in range(1, NUM_CLASSES):
cls_scores = confs[:, c]
score_idx = cls_scores > 0.6
# cls_boxes = tf.boolean_mask(boxes, score_idx)
# cls_scores = tf.boolean_mask(cls_scores, score_idx)
cls_boxes = boxes[score_idx]
cls_scores = cls_scores[score_idx]
nms_idx = compute_nms(cls_boxes, cls_scores, 0.45, 200)
cls_boxes = tf.gather(cls_boxes, nms_idx)
cls_scores = tf.gather(cls_scores, nms_idx)
cls_labels = [c] * cls_boxes.shape[0]
out_boxes.append(cls_boxes)
out_labels.extend(cls_labels)
out_scores.append(cls_scores)
out_boxes = tf.concat(out_boxes, axis=0)
out_scores = tf.concat(out_scores, axis=0)
boxes = tf.clip_by_value(out_boxes, 0.0, 1.0).numpy()
classes = np.array(out_labels)
scores = out_scores.numpy()
return boxes, classes, scores
# Model을 정의하게 되고 실제 Detection한 Image의 결과와 Localization, Label 등을 저장하게 된다.
if __name__ == '__main__':
with open('./config.yml') as f:
cfg = yaml.load(f)
config = cfg['SSD300']
default_boxes = generate_default_boxes(config)
batch_generator, info = create_batch_generator(
args.data_dir, default_boxes,
BATCH_SIZE, args.num_examples, mode='test')
try:
ssd = create_ssd(NUM_CLASSES,
args.pretrained_type,
args.checkpoint_dir,
args.checkpoint_path)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
print('The program is exiting...')
sys.exit()
os.makedirs('outputs/images', exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs('outputs/detects', exist_ok=True)
visualizer = ImageVisualizer(info['idx_to_name'], save_dir='outputs/images')
for i, (filename, imgs, gt_confs, gt_locs) in enumerate(
tqdm(batch_generator, total=info['length'],
desc='Testing...', unit='images')):
boxes, classes, scores = predict(imgs, default_boxes)
filename = filename.numpy()[0].decode()
original_image = Image.open(
os.path.join(info['image_dir'], '{}.jpg'.format(filename)))
boxes *= original_image.size * 2
visualizer.save_image(
original_image, boxes, classes, '{}.jpg'.format(filename))
log_file = os.path.join('outputs/detects', '{}.txt')
for cls, box, score in zip(classes, boxes, scores):
cls_name = info['idx_to_name'][cls - 1]
with open(log_file.format(cls_name), 'a') as f:
f.write('{} {} {} {} {} {}\n'.format(
filename,
score,
*[coord for coord in box]))
참조: 원본코드
코드에 문제가 있거나 궁금한 점이 있으면 wjddyd66@naver.com으로 Mail을 남겨주세요.

Leave a comment