본 글은 Captain Pangyo 블로그 을 보고 연습한 글입니다.
JavaScript
HTML과 CSS는 정적인 언어이다. 정적이라는 것은 브라우저를 통해서 화면에 출력하는 것이지 그 값을 변경시킬 수 없다는 의미이다.
HTML 뼈대
CSS 디자인
JavaScript 웹의 동작
자바스크립트의 특징
자바스크립트는 객체 기반의 스크립트 언어이다.
자바스크립트는 동적이며, 타입을 명시할 필요가 없는 인터프리터 언어이다.
자바스크립트는 객체 지향적 프로그래밍과 함수형 프로그래밍을 모두 표현 가능하다.
자바스크립트 타입
기본 타입
Number - 실수
String - 문자열
Boolean - True, False
undefined - 변수에 값이 할당되지 않을 때 자동으로 할당되는 값
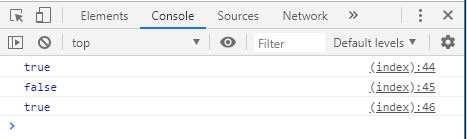
null - 개발자가 의도적으로 할당하는 값. typeof 값이 Object 로 반환. 따라서 === 로 확인
1
2
3
var nullCheck = null ;
console . log ( typeof nullCheck === null );
console . log ( nullCheck === null );
참조 타입(객체 타입)
Object
Array - 배열도 객체로 취급
Function - 함수도 객체로 취급
Object 끼리는 값이 같아도 객체는 다르다고 판단된다. => 주소가 다르기 때문이다.이러한 실제 위치를 가르키는 것을 포인터(Pointer)라고 한다.
1
2
3
4
5
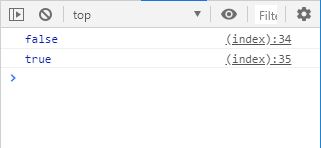
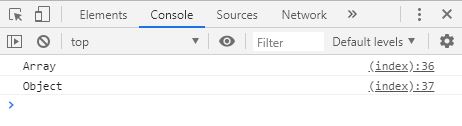
var objA = { value : 20 };
var objB = { value : 20 };
console . log ( objA == objB );
objA = objB ;
console . log ( objA == objB );
NaN (Not a Number)
수치 연산을 해서 정상적인 값을 얻지 못할 때 발생하는 에러
1
2
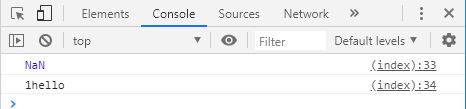
console . log ( 1 - ' hello ' ); // NaN
console . log ( 1 + ' hello ' ); // 1hello
delete 연산자
객체 프로퍼티를 삭제하는 기능. 객체 삭제는 불가능
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
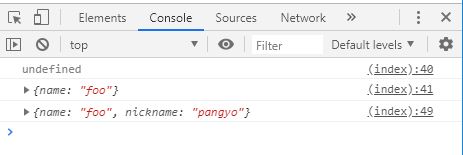
// 1. 객체 프로퍼티를 삭제
var foo = {
name : ' foo ' ,
nickname : ' pangyo '
};
delete foo . nickname ;
console . log ( foo . nickname );
console . log ( foo ); // {name: "foo"}
// 2. delete 로 객체를 삭제할 경우 (변화 없음)
var foo = {
name : ' foo ' ,
nickname : ' pangyo '
};
delete foo ;
console . log ( foo ); // {name: "foo", nickname: "pangyo"}
객체의 모든 연산은 참조 값을 처리
값 비교시에 사용하는 == 를 적용한 예제를 보자.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
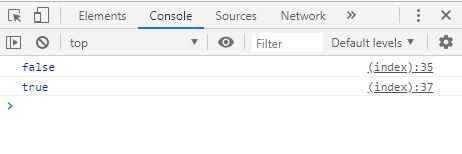
var a = 10 ;
var b = 10 ;
var objA = {
value : 100
};
var objB = {
value : 100
};
var objC = objB ;
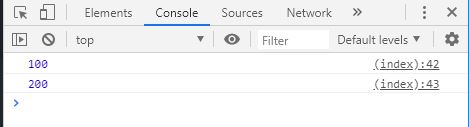
console . log ( a == b ); // true
console . log ( objA == objB ); // false
console . log ( objB == objC ); // true
Array 랑 Object 구분 방법
Array Object
속성 요소
키와 값 값
순서로 구별 키 값으로 구별
1
2
3
4
5
var arr = [];
var obj = {};
console . log ( arr . constructor . name );
console . log ( obj . constructor . name );
delete & splice 연산자 in 배열
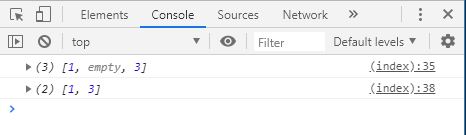
배열에서 delete 를 사용하면 요소의 값만 undefined 로 변경하고, 해당 요소 index 를 지우지는 않는다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
var arr = [ 1 , 2 , 3 ];
delete arr [ 1 ];
console . log ( arr ); // [1, empty, 3]
var arr = [ 1 , 2 , 3 ];
arr . splice ( 1 , 1 );
console . log ( arr ); // [1, 3]
typeof 연산자
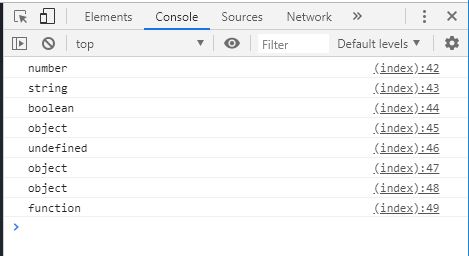
각 데이터 타입에 대한 typeof 수행결과는 다음과 같다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
var num = 10 ;
var str = " a " ;
var boolean = true ;
var obj = {};
var undefined ;
var nullValue = null ;
var arr = [];
function func () {};
console . log ( typeof num ); // number
console . log ( typeof str ); // string
console . log ( typeof boolean ); // boolean
console . log ( typeof obj ); // object
console . log ( typeof undefined ); // undefined
console . log ( typeof nullValue ); // object (null 은 object)
console . log ( typeof arr ); // object (배열도 object)
console . log ( typeof func ); // function
== 연산자와 === 연산자
== 와 === 의 가장 큰 차이점은 값 뿐만 아니라 타입까지 체크하느냐이다.
또한 == 는 수행시에 타입이 다를 경우 타입을 일치시켜 값을 비교하는 특징이 있다.
1
2
console . log ( 1 == ' 1 ' ); // true
console . log ( 1 === ' 1 ' ); // false
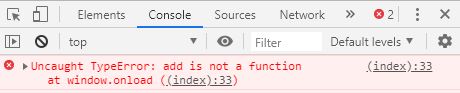
함수 호이스팅
함수 호이스팅이란 함수선언문으로 생성된 함수가 해당 소스의 유효범위의 맨 위로 끌어올려진다.
1
2
3
4
5
add ( 2 , 3 ); // add is not a function
var add = function ( a , b ) {
return a + b ;
};
add ( 4 , 5 );
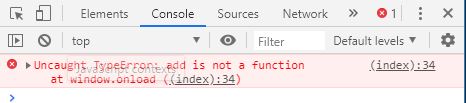
1
2
3
4
5
6
var add ;
add = function ( a , b ) {
return a + b ;
};
console . log ( add ( 4 , 5 ))
console . log ( add ( 2 , 3 ))
1
2
3
4
5
6
var add ;
add = function ( a , b ) {
return a + b ;
};
console . log ( add ( 4 , 5 ))
console . log ( add ( 2 , 3 ))
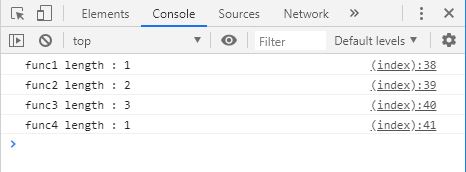
함수의 length 속성
함수의 length란 인수(argument)의 개수이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
function func1 ( a ) { return a ; }
function func2 ( a , b ) { return a + b ; }
function func3 ( a , b , c ) { return a + b + c ; }
function func4 ( a ) { return a + a + a ; }
console . log ( ' func1 length : ' + func1 . length ); // func1 length : 1
console . log ( ' func2 length : ' + func2 . length ); // func2 length : 2
console . log ( ' func3 length : ' + func3 . length ); // func3 length : 3
console . log ( ' func4 length : ' + func4 . length ); // func4 length : 1
내부 함수
함수 내부에 선언한 함수이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
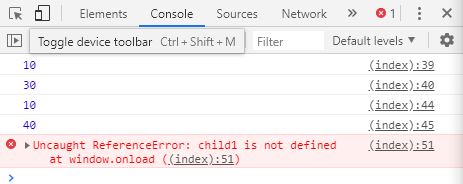
function parent () {
var a = 10 ;
var b = 20 ;
function child1 () {
var b = 30 ;
console . log ( a );
console . log ( b );
}
function child2 () {
var b = 40 ;
console . log ( a );
console . log ( b );
}
child1 ();
child2 ();
}
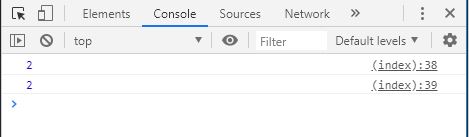
parent (); // 10, 30, 10, 40
child1 (); // child is not defined
생성자 함수
일반 객체 선언과 다르게 여러 개의 객체를 찍어낼 수 있는 함수.
함수명 맨 앞 글자는 대문자, 호출 시에 new 사용.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
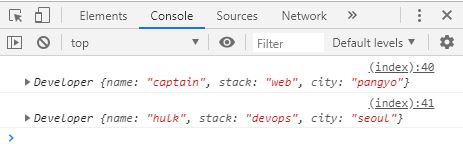
function Developer ( name , stack , city ) {
this . name = name ;
this . stack = stack ;
this . city = city ;
}
var dev = new Developer ( ' captain ' , ' web ' , ' pangyo ' );
var devops = new Developer ( ' hulk ' , ' devops ' , ' seoul ' );
console . log ( dev ); // Developer {name: "captain", stack: "web", city: "pangyo"}
console . log ( devops ); // Developer {name: "hulk", stack: "devops", city: "seoul"}
instaceof
instanceof란 생성자의 prototype 속성이 객체의 프로토타입 어딘가 존재하는지 판별합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
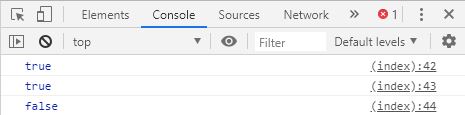
function Car ( make , model , year ) {
this . make = make ;
this . model = model ;
this . year = year ;
}
var auto = new Car ( ' Honda ' , ' Accord ' , 1998 );
var auto2 = new Car ( ' Honda ' , ' Accord ' , 1998 );
var auto3 = Car ( ' Honda ' , ' Accord ' , 1998 );
console . log ( auto instanceof Car ); //true
console . log ( auto2 instanceof Car ); //true
console . log ( auto3 instanceof Car ); //false
instaceof 를 활용한 생성자 함수 구분법
자바스크립트는 생성자 함수 형식이 별도로 없기에 기존 함수에 new만 붙여주면 생성자 함수 생성이 가능하다.
따라서, 생성자 함수가 아닌데 new 를 붙이는 경우를 대비해서 아래와 같은 기법을 적용할 수 있다.
대부분의 오픈소스 라이브러리에서 사용하는 패턴
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
function Func ( arg ) {
// instanceof 로 생성자 함수임을 확인
if ( ! ( this instanceof arguments . callee )) // 'this instanceof 함수명' 도 가능
return new Func ( arg );
this . value = arg || 0 ;
}
var a = new Func ( 100 );
var b = Func ( 200 );
console . log ( a . value );
console . log ( b . value );
프로토타입(Prototype)
자바스크립트는 객체지향 언어이다.프로토타입 체이닝: 해당 함수에 존재하지 않는 속성, 메서드를 부모 객체(Prototype 객체)를 찾음
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
function Person () {}
Person . prototype . eyes = 2 ;
Person . prototype . nose = 1 ;
var kim = new Person ();
var park = new Person ();
console . log ( kim . eyes ); //Kim에 eyes라는 property가 존재하지 않으나 부모 객체의 값을 가져와서 출력하는 것을 볼 수 있다.
console . log ( park . eyes ); // => 2
프로토타입 객체 메서드 재정의
부모에서 정의된 메서드를 자식이 Override하여 재정의 할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
// 부모 클래스
function MyParent () {
this . property1 = ' data1 ' ;
console . log ( ' MyParent ' );
}
MyParent . prototype . method1 = function () {
console . log ( ' property1 = ' + this . property1 );
};
// 자식 클래스
function MyChild () {
console . log ( ' MyChild ' ); }
// 부모 클래스 상속하기 MyChild.prototype = new MyParent();
// 생성자 설정 MyChild.prototype.constructor = MyChild;
/*
------------------ * 메서드 오버라이드 * ------------------
*/
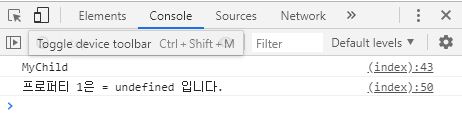
MyChild . prototype . method1 = function () {
console . log ( ' 프로퍼티 1은 = ' + this . property1 + ' 입니다. ' );
};
// 자식 인스턴스 생성
var child = new MyChild ();
// 메서드 호출
child . method1 ();
즉시 실행 함수
함수를 정의함과 동시에 바로 실행하는 함수. 함수를 다시 호출할 수 없다는 특징이 있다.
따라서, 최초 한 번의 실행만 요구되는 초기화 코드에 적합하다.
jQuery 와 같은 오픈소스 라이브러리들의 구조.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
/*
Format
function [name]([param1[, param2[, ..., paramN]]]) {
statements
}
*/
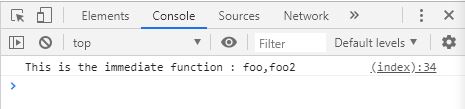
( function ( name ) {
console . log ( ' This is the immediate function : ' + name );
})([ ' foo ' ,[ ' foo2 ' ]]);
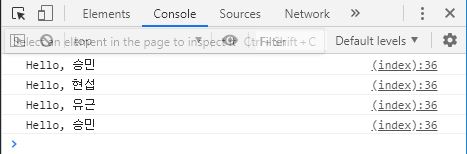
클로져
클로져는 독립적인 변수를 가르키는 함수이다. 또는 클로저 안에 정의된 함수는 만들어진 환경을 기억한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
function Hello ( name ) {
this . _name = name ;
}
Hello . prototype . say = function () {
console . log ( ' Hello, ' + this . _name );
}
var hello1 = new Hello ( ' 승민 ' );
var hello2 = new Hello ( ' 현섭 ' );
var hello3 = new Hello ( ' 유근 ' );
hello1 . say (); // 'Hello, 승민'
hello2 . say (); // 'Hello, 현섭'
hello3 . say (); // 'Hello, 유근'
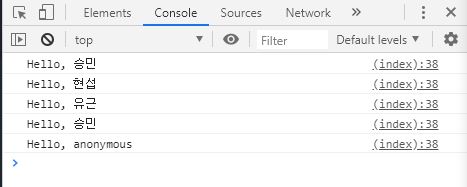
hello1 . name = ' anonymous ' ;
hello1 . say (); // 'Hello, anonymous'
hello1 . _name = ' anonymous ' ;
hello1 . say (); // 'Hello, anonymous'
클로져를 통한 은닉화
클로져가 변수에 접근하기 위해서는 변수명 앞에 underscore(_)를 써서 접근 가능하다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
function Hello ( name ) {
this . _name = name ;
}
Hello . prototype . say = function () {
console . log ( ' Hello, ' + this . _name );
}
var hello1 = new Hello ( ' 승민 ' );
var hello2 = new Hello ( ' 현섭 ' );
var hello3 = new Hello ( ' 유근 ' );
hello1 . say (); // 'Hello, 승민'
hello2 . say (); // 'Hello, 현섭'
hello3 . say (); // 'Hello, 유근'
hello1 . name = ' anonymous ' ;
hello1 . say (); // 'Hello, anonymous'
hello1 . _name = ' anonymous ' ;
hello1 . say (); // 'Hello, anonymous'
실행 컨텍스트를 이해하기 위한 자바스크립트 동작과정
Variable Object: 실행에 필요한 여러 정보들을 담을 객체 생성
변수
Parameter, Argument
함수 선언
Scope Chain: 해당 전역 또는 함수가 참조할 수 있는 변수, 함수선언 등의 정보를 담고있는 전역객체 또는 활성객체의 리스트
this: this 프로퍼티에는 this값이 할당된다. this에 할당되는 값은 함수 호출 패턴에 의해 결정된다.
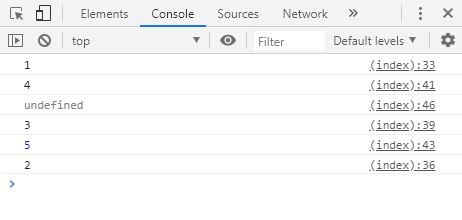
비동기 실행 방식인 setTimeout 를 이용한 예제이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
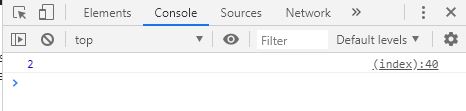
console . log ( " 1 " );
function exec () {
setTimeout ( function () {
console . log ( " 2 " );
}, 3000 );
setTimeout ( function () {
console . log ( " 3 " );
}, 0 );
console . log ( " 4 " );
setTimeout ( function () {
console . log ( 5 );
}, 1000 );
}
console . log ( exec ());
// 위 코드 실행 결과 : 1, 4, 3, 5, 2
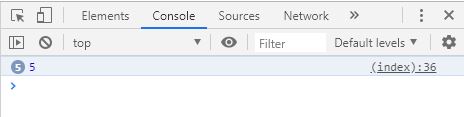
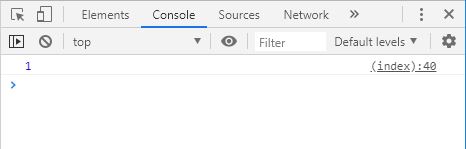
이번엔 for 문과 setTimeout 이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
var i ;
for ( i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i ++ ) {
setTimeout ( function () {
console . log ( i ); // 5, 5, 5, 5, 5
}, 1000 );
}
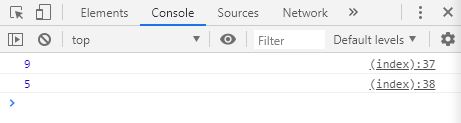
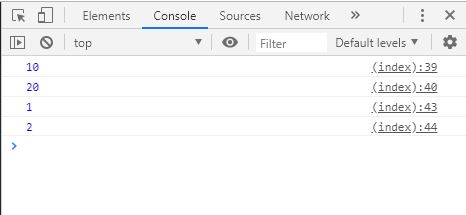
arguments 객체
함수 호출시에 넘겨진 실제 인자 값을 가진 배열
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
function sum () {
for ( var i = 0 , result = 0 ; i < arguments . length ; i ++ ) {
result += arguments [ i ];
}
return result ;
}
console . log ( sum ( 1 , 2 , 3 )); // 6
console . log ( sum ( 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 )); // 21
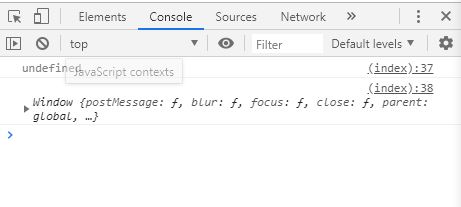
apply() & call()
다른 객체 대신 메소드를 호출하는데 사용된다.
종류 구문 매게변수
call
fun.call([thisObj[, arg[, arg2[, ...]]]
fun: 가져다 쓸 메소드
thisObj(선택 사항): 현재 객체로 사용될 객체
arg1,arg2,argN(선택 사항): 메소드에 전달될 인수 목록
apply
fun.apply([thisObj[,argArray]])
fun: 가져다 쓸 메소드
thisObj(선택 사항): 현재 객체로 사용될 객체
argArray: 메소드에 전달될 인수 집합
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
function sum () {
var args1 = Array . apply ( arguments );
args1 . push ( 100 ); // 0: 100
console . dir ( args1 ); // Array(1)
var args2 = Array . prototype . slice . apply ( arguments );
args2 . push ( 100 ); // 3: 100
console . dir ( args2 ); // Array(4)
}
sum ( 1 , 2 , 3 );
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
function user ( firstName , lastName , age ) {
this . firstName = firstName ;
this . lastName = lastName ;
}
user . apply ( window , [ ' pangyo ' , ' captain ' ]); // user.call(window, 'John', 'Doe'); 와 같음
console . log ( window . firstName ); // 'pangyo'
console . log ( window . lastName ); // 'captain'
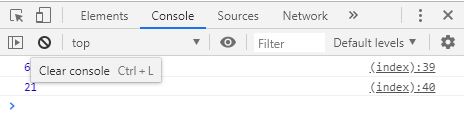
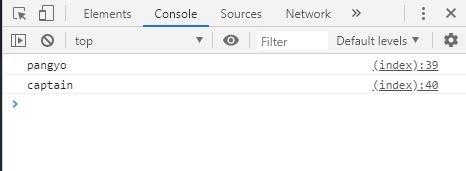
this 바인딩
일반적으로 함수 내부에서 this를 사용하면 전역 스코프(window)에 접근한다.하지만 현재 작업하고 있는 환경에서는 this가 적용되지 않았다. Online Complier 환경에서 Complie하고 있어서 생기는 문제인 것 같다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
// 함수 선언식
var text = ' global ' ;
function binding () {
var text = ' local ' ;
console . log ( this . text ); // 'global'
console . log ( this ); // Window {stop: ƒ, open: ƒ, alert: ƒ, confirm: ƒ, prompt: ƒ, …}
}
binding ();
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
var text = ' global ' ;
var binding = {
text : ' local ' ,
printText : function () {
console . log ( this . text ); // 'local'
console . log ( this ); // {text: "local", printText: ƒ}
}
};
binding . printText ();
스코프 체인을 이해하기 위한 예제
스코프 체인이란 실행 시점에서 identifiers(식별자)를 찾는 것이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
// ex.1
var a = 1 ;
var b = 2 ;
function func () {
var a = 10 ;
var b = 20 ;
console . log ( a ); // 10
console . log ( b ); // 20
}
func ();
console . log ( a ); // 1
console . log ( b ); // 2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
// ex.2
var a = 1 ;
function func () {
var a = 2 ;
function innerfunc () {
return a ;
}
console . log ( innerfunc ()); // 2
}
func ();
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
// ex.3
var a = 1 ;
function func1 () {
return a ;
}
function func2 ( func1 ) {
var a = 2 ;
console . log ( func1 ()); // 1
}
func2 ( func1 );
내용 참조: Captain Pangayo 블로그 TCP School Jsfiddle Code DailyEngineering 블로그 버미노트 블로그


Leave a comment