Paper33. CONTRASTIVE REPRESENTATION DISTILLATION-Code
CONTRASTIVE REPRESENTATION DISTILLATION - Code
출처: CONTRASTIVE REPRESENTATION DISTILLATION
코드: HobbitLong GitHub
해당 Blog의 Code는 원본 Code를 간략히 하여 실제 사용한 Code를 기반으로 작성하였습니다. 원본 Code와 약간 다른점이 있습니다.
Model
Model은 기본적인 ANN으로 구성하였습니다. 기존의 Model들과 다른점은 forward과정에서 is_feat=True인 경우, Probability뿐만 아니라 Contrastive Learning을 위하여 Embedding값도 return합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
################# Model #################
def xavier_init(m):
if type(m) == nn.Linear:
nn.init.xavier_normal_(m.weight)
if m.bias is not None:
m.bias.data.fill_(0.0)
class Layer(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_dim, h_dim):
super(Layer, self).__init__()
self.linear = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_dim, h_dim),
nn.BatchNorm1d(h_dim),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True))
self.linear.apply(xavier_init)
def forward(self, x):
return self.linear(x)
class ANN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_hidden_list):
super(ANN, self).__init__()
self.Layer_List = nn.ModuleList(
[Layer(in_hidden, in_hidden_list[i + 1]) for i, in_hidden in enumerate(in_hidden_list[:-1])])
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_features=in_hidden_list[-1], out_features=1),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
self.embedding_num = len(in_hidden_list) - 1
def forward(self, x, is_feat=False):
f_ = dict()
f_list = []
for num in range(self.embedding_num):
if num == 0:
f_[num] = self.Layer_List[num](x)
else:
f_[num] = self.Layer_List[num](f_[num - 1])
f_list.append(f_[num])
output = self.classifier(f_[num])
if is_feat:
return f_list, output
else:
return output
KL-Divergence Loss
KL-Divergence에 Temperature probability를 적용하여 계산하였다. Distilling the Knowledge in a Neural Network에서도 temperature probability를 사용하였다.
T=1인 경우 Softmax와 동일하고, T: 2~4인 경우 distillation하기에 최적의 temperature라고 설명하고 있다. (논문에서는 default값으로 4를 사용하였다.)
Appendix. Softmax with Temperature Parameter
Temperature가 커질수록 각 확률들의 차이가 줄어든다. 하지만, 순서는 변하지 않기 때문에 정확도에 영향을 주지 않는다.
아래 그림은 점차적으로 temperature를 키우면서 visualization한 경우이다.
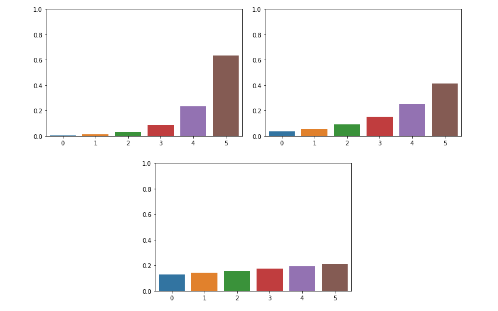
참조: 3months Blog
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
class DistillKL(nn.Module):
"""Distilling the Knowledge in a Neural Network"""
def __init__(self, T):
super(DistillKL, self).__init__()
self.T = T
def forward(self, y_s, y_t):
p_s = F.log_softmax(y_s/self.T, dim=1)
p_t = F.softmax(y_t/self.T, dim=1)
loss = F.kl_div(p_s, p_t, size_average=False) * (self.T**2) / y_s.shape[0]
return loss
Student Model Train
CFG: Hyperparameterteacher_model = ANN([CFG['In_Hidden']] + [256, 1024, 256]).to(device): Teacher model after trainingcriterion_cls = nn.BCELoss(): Classification Losscriterion_div = DistillKL(CFG["kd_T"]): KL divergence Losscriterion_kd = CRDLoss(opt): CRD(CONTRASTIVE REPRESENTATION DISTILLATION) Loss
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
for i, hyper_parameter in enumerate(tqdm(hyperparameter_list, desc='Hyperparameter Search...')):
# Hyperparameter
CFG['LEARNING_RATE'] = hyper_parameter['lr']
CFG['MIN_LR'] = hyper_parameter['min_lr']
CFG['REG'] = hyper_parameter['reg']
CFG['In_hidden_list'] = hyper_parameter['dimension']
# Fixed Teacher Model
teacher_model = ANN([CFG['In_Hidden']] + [256, 1024, 256]).to(device)
teacher_model.load_state_dict(torch.load('./Result/Model/Teacher/teacher.pth'))
teacher_model.eval()
# Student Model
student_model = ANN([CFG['S_In_Hidden']] + CFG['In_hidden_list'])
student_model.eval()
module_list = nn.ModuleList([])
module_list.append(student_model)
trainable_list = nn.ModuleList([])
trainable_list.append(student_model)
criterion_cls = nn.BCELoss()
criterion_div = DistillKL(CFG["kd_T"])
for X_t, X_s, y in train_loader:
break
feat_t, _ = teacher_model(X_t.to(device), is_feat=True)
feat_s, _ = student_model(X_s, is_feat=True)
opt['s_dim'] = feat_s[-1].shape[1]
opt['t_dim'] = feat_t[-1].shape[1]
criterion_kd = CRDLoss(opt)
module_list.append(criterion_kd.embed_s)
module_list.append(criterion_kd.embed_t)
trainable_list.append(criterion_kd.embed_s)
trainable_list.append(criterion_kd.embed_t)
criterion_list = nn.ModuleList([])
criterion_list.append(criterion_cls) # classification loss
criterion_list.append(criterion_div) # KL divergence loss, original knowledge distillation
criterion_list.append(criterion_kd)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(student_model.parameters(), lr=CFG['LEARNING_RATE'])
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer, mode='max', factor=0.5, patience=1,
threshold_mode='abs', min_lr=1e-6, verbose=False)
module_list.append(teacher_model)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
module_list.to(device)
criterion_list.to(device)
cudnn.benchmark = True
best_student_model, S_F1 = student_train(contrasitive_data_loader, val_loader, module_list, criterion_list,
optimizer, opt, scheduler, device, CFG)
CRD Loss - 1
f_s: \(S \in \mathbb{R}^{\text{batch size} \times \text{student dim}}\), (CRDLoss - forward input1)f_t: \(T \in \mathbb{R}^{\text{batch size} \times \text{teacher dim}}\), (CRDLoss - forward input2)f_s = self.embed_s(f_s): \(g(T) \in \mathbb{R}^{\text{batch size} \times \text{embedding dim}}\): Teacher latent representation -> Embeddingf_t = self.embed_t(f_t): \(g(S) \in \mathbb{R}^{\text{batch size} \times \text{embedding dim}}\): Student latent representation -> Embedding
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
class Embed(nn.Module):
"""Embedding module"""
def __init__(self, dim_in=1024, dim_out=128):
super(Embed, self).__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(dim_in, dim_out)
self.l2norm = Normalize(2)
def forward(self, x):
x = x.view(x.shape[0], -1)
x = self.linear(x)
x = self.l2norm(x)
return x
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
################# Loss Function #################
class CRDLoss(nn.Module):
"""CRD Loss function
includes two symmetric parts:
(a) using teacher as anchor, choose positive and negatives over the student side
(b) using student as anchor, choose positive and negatives over the teacher side
Args:
opt.s_dim: the dimension of student's feature
opt.t_dim: the dimension of teacher's feature
opt.feat_dim: the dimension of the projection space
opt.nce_k: number of negatives paired with each positive
opt.nce_t: the temperature
opt.nce_m: the momentum for updating the memory buffer
opt.n_data: the number of samples in the training set, therefor the memory buffer is: opt.n_data x opt.feat_dim
"""
def __init__(self, opt):
super(CRDLoss, self).__init__()
self.embed_s = Embed(opt['s_dim'], opt['feat_dim'])
self.embed_t = Embed(opt['t_dim'], opt['feat_dim'])
self.contrast = ContrastMemory(opt['feat_dim'], opt['n_data'], opt['nce_k'], opt['nce_t'], opt['nce_m'])
self.criterion_t = ContrastLoss(opt['n_data'])
self.criterion_s = ContrastLoss(opt['n_data'])
def forward(self, f_s, f_t, idx, contrast_idx=None):
"""
Args:
f_s: the feature of student network, size [batch_size, s_dim]
f_t: the feature of teacher network, size [batch_size, t_dim]
idx: the indices of these positive samples in the dataset, size [batch_size]
contrast_idx: the indices of negative samples, size [batch_size, nce_k]
Returns:
The contrastive loss
"""
f_s = self.embed_s(f_s)
f_t = self.embed_t(f_t)
out_s, out_t = self.contrast(f_s, f_t, idx, contrast_idx)
s_loss = self.criterion_s(out_s)
t_loss = self.criterion_t(out_t)
loss = s_loss + t_loss
return loss
CRD Loss - 2
ContrastMemory는 implementation을 위한 memory buffer이다.
inputSize: Total number of training datasetoutputSize: \(\in \mathbb{R}^{\text{embedding dim}}\), Embedding diemnsionK: \(\in \mathbb{R}^{N}\), # of negative samplesT: \(\gamma\), Temperature that adjusts the concentration levely: \(\in \mathbb{R}^{\text{batch size}}\): The indices of these positive samples in the datasetidx: \(g(S) \in \mathbb{R}^{\text{batch size} \times (\text{N+1})}\): The indices of negative samplestorch.rand(outputSize, inputSize).mul_(2 * stdv).add_(-stdv): mean: 0, std: stdv인 uniform distributionweight_v1: Memory buffer를 사용하기 위하여 memory에서 해당되는 sample을 indexing하는 과정이다. positive인 경우에는 나중에 update하게 된다. 즉, 한번 epoch가 돈 이후에는 positive sample만 들어와도 저장되어있는 negative sample의 값을 가져와 사용할 수 있다.out_v2 = torch.bmm(weight_v1, v2.view(batchSize, inputSize, 1)): \(g^T(T)' g^S(S)\)out_v2 = torch.exp(torch.div(out_v2, T)): \(e^{g^T(T)' g^S(S)/\gamma}\)out_v1 = torch.div(out_v1, Z_v1).contiguous(): 본문에는 \(\frac{e^{g^T(T)' g^S(S)/\gamma}}{e^{g^T(T)' g^S(S)/\gamma} + \frac{N}{M}}\)로 적혀있었지만, 구현에서는 해당 Code와 같이 나타내어 [0~1]사이의 값으로 나타내었다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
################# For Loss Function #################
class ContrastMemory(nn.Module):
"""
memory buffer that supplies large amount of negative samples.
"""
def __init__(self, inputSize, outputSize, K, T=0.07, momentum=0.5):
super(ContrastMemory, self).__init__()
self.nLem = outputSize
self.K = K
self.register_buffer('params', torch.tensor([K, T, -1, -1, momentum]))
stdv = 1. / math.sqrt(inputSize / 3)
self.register_buffer('memory_v1', torch.rand(outputSize, inputSize).mul_(2 * stdv).add_(-stdv))
self.register_buffer('memory_v2', torch.rand(outputSize, inputSize).mul_(2 * stdv).add_(-stdv))
def forward(self, v1, v2, y, idx=None):
K = int(self.params[0].item())
T = self.params[1].item()
Z_v1 = self.params[2].item()
Z_v2 = self.params[3].item()
momentum = self.params[4].item()
batchSize = v1.size(0)
outputSize = self.memory_v1.size(0)
inputSize = self.memory_v1.size(1)
# sample
weight_v1 = torch.index_select(self.memory_v1, 0, idx.view(-1)).detach()
weight_v1 = weight_v1.view(batchSize, K + 1, inputSize)
out_v2 = torch.bmm(weight_v1, v2.view(batchSize, inputSize, 1))
out_v2 = torch.exp(torch.div(out_v2, T))
# sample
weight_v2 = torch.index_select(self.memory_v2, 0, idx.view(-1)).detach()
weight_v2 = weight_v2.view(batchSize, K + 1, inputSize)
out_v1 = torch.bmm(weight_v2, v1.view(batchSize, inputSize, 1))
out_v1 = torch.exp(torch.div(out_v1, T))
# set Z if haven't been set yet
if Z_v1 < 0:
self.params[2] = out_v1.mean() * outputSize
Z_v1 = self.params[2].clone().detach().item()
print("normalization constant Z_v1 is set to {:.1f}".format(Z_v1))
if Z_v2 < 0:
self.params[3] = out_v2.mean() * outputSize
Z_v2 = self.params[3].clone().detach().item()
print("normalization constant Z_v2 is set to {:.1f}".format(Z_v2))
# compute out_v1, out_v2
out_v1 = torch.div(out_v1, Z_v1).contiguous()
out_v2 = torch.div(out_v2, Z_v2).contiguous()
# update memory
with torch.no_grad():
l_pos = torch.index_select(self.memory_v1, 0, y.view(-1))
l_pos.mul_(momentum)
l_pos.add_(torch.mul(v1, 1 - momentum))
l_norm = l_pos.pow(2).sum(1, keepdim=True).pow(0.5)
updated_v1 = l_pos.div(l_norm)
self.memory_v1.index_copy_(0, y, updated_v1)
ab_pos = torch.index_select(self.memory_v2, 0, y.view(-1))
ab_pos.mul_(momentum)
ab_pos.add_(torch.mul(v2, 1 - momentum))
ab_norm = ab_pos.pow(2).sum(1, keepdim=True).pow(0.5)
updated_v2 = ab_pos.div(ab_norm)
self.memory_v2.index_copy_(0, y, updated_v2)
return out_v1, out_v2
CRD Loss - 3
CRD Loss를 최종적으로 계산하는 Code이다. 주요한 점은 Input으로 들어오는 값은 [positive sample, N 개의 negative sample]로서 들어온다는 것이다. 즉, 1번째 index만 positive sample이고, 나머지는 negative sample이다.
n_data: \(\in \mathbb{R}^{\text{batchsize} \times (\text{N+1}) \times 1}\): \(h(T,S)\)log_D1 = torch.div(P_pos, P_pos.add(m * Pn + eps)).log_(): \(\mathbb{E}_{q(T,S|C=1)}[\log h(T,S)]\)log_D0 = torch.div(P_neg.clone().fill_(m * Pn), P_neg.add(m * Pn + eps)).log_(): \(N \mathbb{E}_{q(T,S|C=0)} [1-\log(h(T,S))]\)
Appendix. Pn을 사용하여 완전히 나타낸 것은 아니다. 하지만 하나의 epoch가 다 돌게되면 \(\sum_{i=1}^{\text{batch size}} \text{log_D1}_i\)의 값이\(\mathbb{E}_{q(T,S|C=1)}[\log h(T,S)]\)의 값과 비슷해 질 이다. (batch단위로 update되면서 조금씩 바뀐다.)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
class ContrastLoss(nn.Module):
"""
contrastive loss, corresponding to Eq (18)
"""
def __init__(self, n_data):
super(ContrastLoss, self).__init__()
self.n_data = n_data
def forward(self, x):
bsz = x.shape[0]
m = x.size(1) - 1
# noise distribution
Pn = 1 / float(self.n_data)
# loss for positive pair
P_pos = x.select(1, 0)
log_D1 = torch.div(P_pos, P_pos.add(m * Pn + eps)).log_()
# loss for K negative pair
P_neg = x.narrow(1, 1, m)
log_D0 = torch.div(P_neg.clone().fill_(m * Pn), P_neg.add(m * Pn + eps)).log_()
loss = - (log_D1.sum(0) + log_D0.view(-1, 1).sum(0)) / bsz
return loss

Leave a comment