Paper08. Alzhimer’s Disease CNN
Convolutional neural networks for classification of Alzheimer’s disease: Overview and reproducible evaluation
Convolutional neural networks for classification of Alzheimer’s disease: Overview and reproducible evaluation
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1361841520300591#bib0003)
Abstract
Numerous machine learning (ML) approaches have been proposed for automatic classification of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) from brain imaging data. In particular, over 30 papers have proposed to use convolutional neural networks (CNN) for AD classification from anatomical MRI. However, the classification performance is difficult to compare across studies due to variations in components such as participant selection, image preprocessing or validation procedure. Moreover, these studies are hardly reproducible because their frameworks are not publicly accessible and because implementation details are lacking. Lastly, some of these papers may report a biased performance due to inadequate or unclear validation or model selection procedures. In the present work, we aim to address these limitations through three main contributions. First, we performed a systematic literature review. We identified four main types of approaches: i) 2D slice-level, ii) 3D patch-level, iii) ROI-based and iv) 3D subject-level CNN. Moreover, we found that more than half of the surveyed papers may have suffered from data leakage and thus reported biased performance. Our second contribution is the extension of our open-source framework for classification of AD using CNN and T1-weighted MRI. The framework comprises previously developed tools to automatically convert ADNI, AIBL and OASIS data into the BIDS standard, and a modular set of image preprocessing procedures, classification architectures and evaluation procedures dedicated to deep learning. Finally, we used this framework to rigorously compare different CNN architectures. The data was split into training/validation/test sets at the very beginning and only the training/validation sets were used for model selection. To avoid any overfitting, the test sets were left untouched until the end of the peer-review process. Overall, the different 3D approaches (3D-subject, 3D-ROI, 3D-patch) achieved similar performances while that of the 2D slice approach was lower. Of note, the different CNN approaches did not perform better than a SVM with voxel-based features. The different approaches generalized well to similar populations but not to datasets with different inclusion criteria or demographical characteristics. All the code of the framework and the experiments is publicly available: general-purpose tools have been integrated into the Clinica software (www.clinica.run) and the paper-specific code is available at: https://github.com/aramis-lab/AD-DL.
해당논문에서 강조하는 부분은 크게 3가지 이다.
- 해당 논문은 최근에 나온 Alzhimer’s Disease를 CNN으로서 Classification하는 논문에 대하여 review한다. 하지만 많은 논문이 Experiment Setting에서 잘못한 결과를 발표하고 있다. 가장 대표적으로 Biased된 결과를 성능이 좋은 Model이라고 평가하고 있다.
- 해당 논문은 이러한 문제를 해결하기 위하여 Image Preprocessing => Download & Preprocessing & Split하는 Tool을 제공한다. 이러한 Tool을 많은 논문이 사용함으로써, reconstruction이 가능하다.
- 모든 Experiment를 동일하게 고정하고 결과를 비교해본 결과, SVM(voxel-based features)과 별로 차이를 보이지 않는다. => CNN으로서 Model을 구축하는 것은 단순히 Overfitting된 결과일 확률이 높다.
Introduction
해당 논문에서 많은 논문이 reconstruction이 불가능한 이유를 크게 4가지로서 설명하고 있다.
- Sets of participants
- Image preprocessing procedures
- Cross-Validation
- Reported Evaluation Metrics
즉, 사용하고자 하는 Dataset의 Subject가 다르며, Image preprocessing방법이 모두 다르다는 것 이다. 이것은 Dataset의 한계로서 어쩔 수 없으며, Dataset에 따라 많은결과의 차이를 보일 것 이다.
Cross-Validation의 경우에는 많은 Experiment에서 Dataset이 작아서 어쩔수 없이 발생하는 문제이다. 하지만, 문제는 Validation으로서 사용하지 않고 이러한 Validation을 TestDataset으로서 사용한 논문들이 존재한다는 것 이다.
Reported Evaluation Metrics의 문제는 Dataset이 Unbalance한 경우에도 Accuracy와 같은 Metrics을 사용함으로 인하여, Model의 정확한 성능을 측정하지 못했다는 것 이다.
해당 논문에서는 다음과 같은 문제를 해결하기 위하여 결국 자신의 Tool을 소개하는 것이 목적이다.
해당논문에서는 Train: ADNI -> Test: ADNI or AIBL, OASIS로서 Experiment를 Setting하고, Image Preprocessing 혹은 Data Split까지 모두 지원하는 Tool을 제공하고 있다고 이야기 하고 있다. 또한, 이러한 Tool을 사용하여 CNN및 다른 Model의 성능을 비교하고 있다.
State of the art
해당 논문을 읽는 가장 큰 이유이다. 해당 논문에서는 최근의 Alzhimer’s Disease에 관하여 모든 논문을 정리하고 잘못된 부분에 대하여 분류하였다.
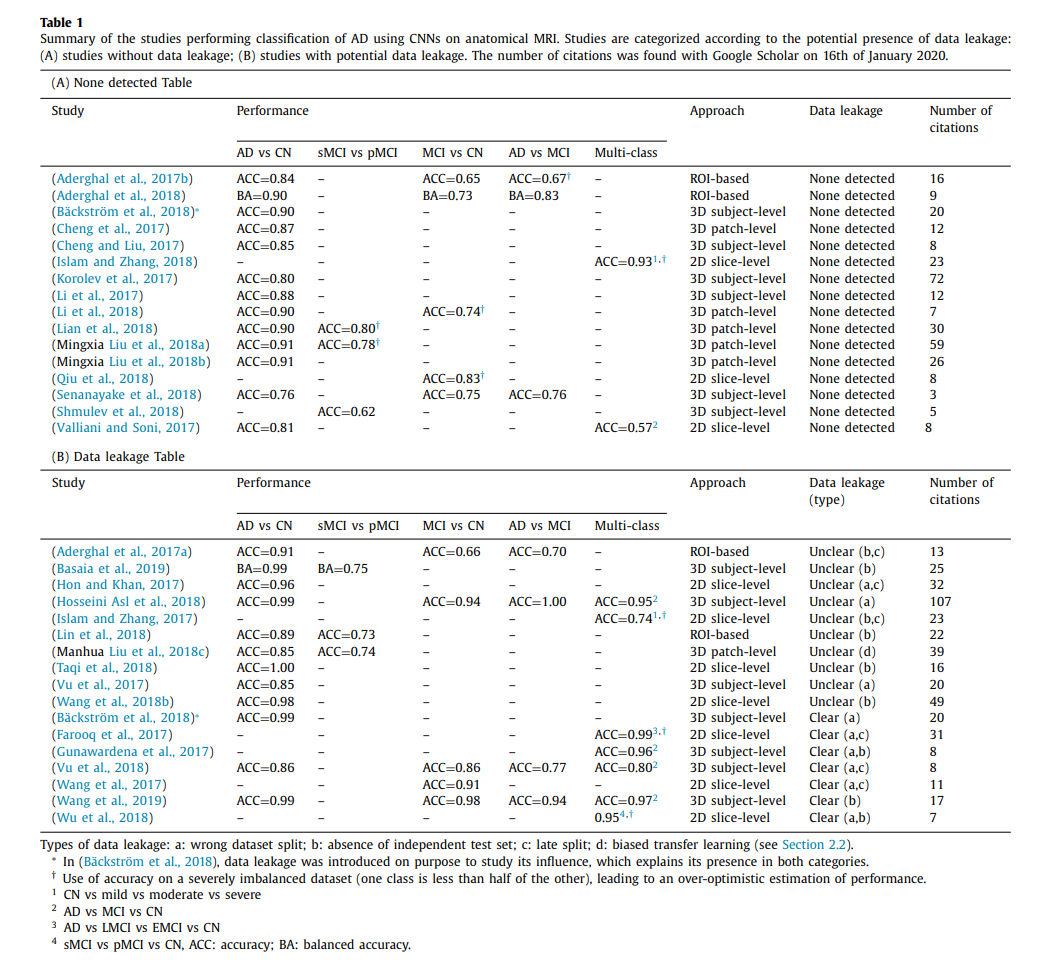
위의 Image를 보게 되면 크게 몇가지로 분류하여 Performance에 대하여 적어두었다.
1. Data Leakage
논문에서 정의하는 Data Leakage는 쉽게 말해서 Cheating을 하였다고 볼 수 있는 부분이다. 이러한 Data Leakage에 대하여 크게 4가지로 분류하였다
- Wrong Data Split: Train & Validation & Test Split에 대하여 Subject Level로서 이루워지지 않았다는 것 이다. 즉, 3D MRI를 2D Slice로서 Split하고 적용할 때, 하나의 Subject의 값이 Train & Validation & Test에 들어가거나, 하나의 Subject가 여러 번 들어가는 경우도 포함되게 된다.
- Late Split: Data Augmentation, Feature Selection, Auto Encoder의 Train, Test와 Classification에서의 Train, Test가 다른 경우이다.
- Biased Transfer Learning: 어려운 문제를 먼저 Training하기 위하여 CN vs AD에 대하여 Training후에 Test를 CN vs MCI로서 수행하게 되는 경우, CN이 Train과 Test에 모두 포함되는 Subject가 있는 경우이다.
- Absence of an independent test set: Hyperparameter를 Search하는데에서 Validation Set이 아닌, Test Set을 사용하는 경우이다.
2. Main Classification Performance
Classification Task의 Performance이다.
- AD vs CN
- sMCI vs pMCI
- MCI vs CN
- AD vs MCI
- Multi-Class
3. Classification of AD with end-to-end CNNs
각각의 방법에 대하여 간략히 설명하면 다음과 같다.
-
2D slice-level CNN: MRI은 3D Volumne이다. 이것을 2D로서 Slice로서 Split하여 사용하면, 기존의 CNN Architecture(Pre-Train)를 사용할 수 있다는 장점이 있다. 하지만, 어떤 axial로서 Slice할지 또한 Subject-level로서 Performance를 측정하였는지, Slice-level로서 Performance를 측정하였는지에 대하여 Performance가 많이 달라지게 된다. => 다른 논문들과 비교가 어렵다.
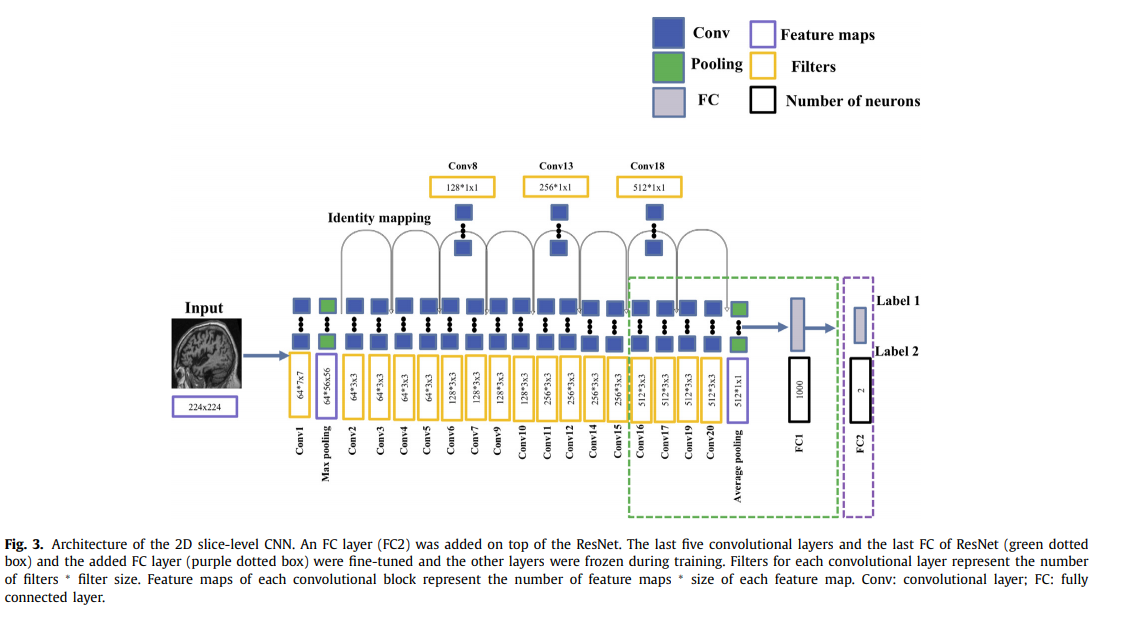
-
3D path-level CNN: MRI를 3D Volume으로서 그대로 사용하는 것은, Dataset의 Feature가 많고 Sparse하다는 단점이 발생하게 된다. 따라서, 3D patch로서 잘라서 사용하게 되면 Memory를 줄일수 있고, Parameter를 줄여서 overfitting을 방지할 수 있다는 장점이 생기게 된다. 하지만, 현재 논문들은 많은 Patch를 하나의 CNN Architecture에 넣고 있고, 각각의 다른 CNN으로서 학습하지 않고 있다는 단점이 있다.
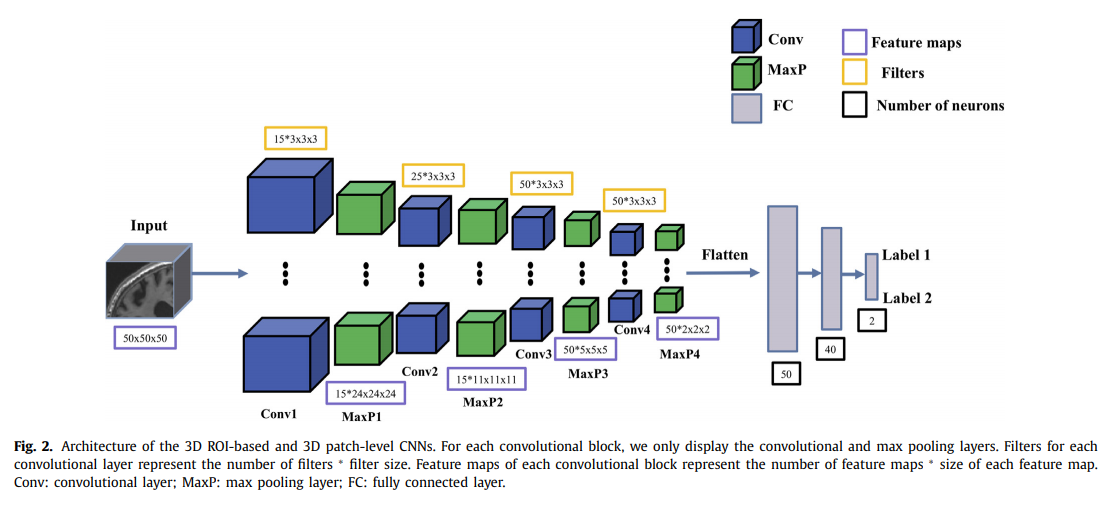
-
ROI-based CNN: 3D patch를 사용하여, Dataset을 줄인다고 하여도, 이것은 Informative한 Dataset이라고 말할 수 없다. 따라서 ROI based CNN은 해당 MRI에서 관심있는 ROI만을 추출하여, CNN Classification을 수행하는 방법이다. AD에 관련된 Hippocampus혹은 Multi-ROI로서는 CSF까지 추가하여 CNN Model을 구축하고 있다. 몇몇 논문에서는 ROI를 sagittal, coronal and aixal로서 2D로 Slice한 뒤, 각각의 CNN Architecture를 Training한 뒤, Merge하여 Performance를 높이는 방식으로 이루워지기도 한다.
-
3D-Subject-level CNN: High resource를 사용할 수 있는 현재에는 3D Volume을 그대로 사용하는 Paper도 몇몇 존재한다. 하지만, 아직 Performance가 높지 않고, 3D Volume을 그대로 사용하는 대부분의 논문은 AutoEncoder로서 Feature Reduction을 실시한 뒤 CNN을 사용하는 경향을 보인다.
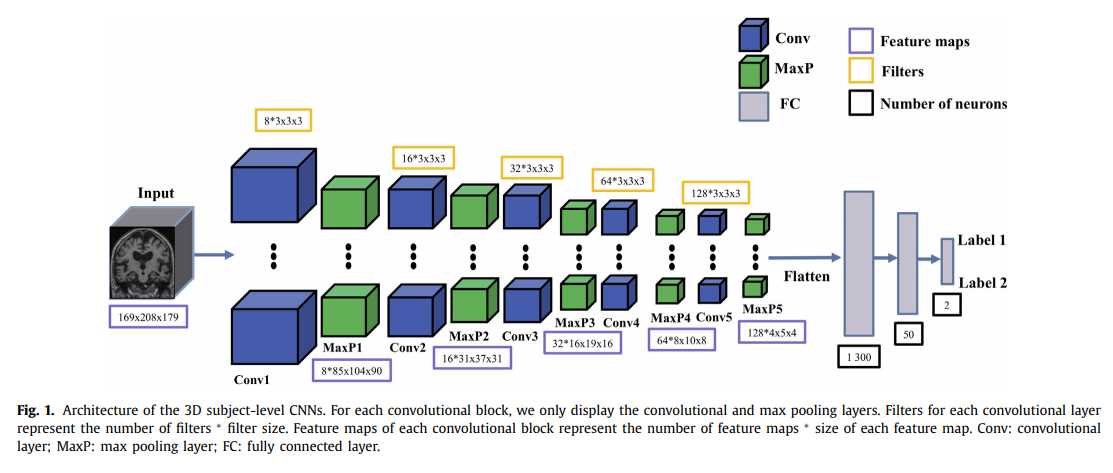
2D Slice, 3D ROI-based(Left, Right of Hippocampus), 3D Patch-level의 경우 하나의 Subject에서 여러 output이 나올 수 있다. 이런 경우 해당 논문의 Experiment는 Subject를 기준으로 Performance를 평가하기 위하여, Soft Voting을 적용하였다.
Comparison to a linear SVM on voxel-based features
DL Model인 CNN과 비교하기 위하여 ML방법인 SVM을 사용하였다. 하지만, 이러한 방식은 3D Volume 혹은 MRI Image를 그대로 사용하게 되면, 너무 High-Dimension이므로 이전 방식인 Clinical(https://github.com/aramis-lab/clinica)인 Open Source인 자신들의 방법을 제시하였다.
결과를 살펴보게 되면, 다음과 같다.
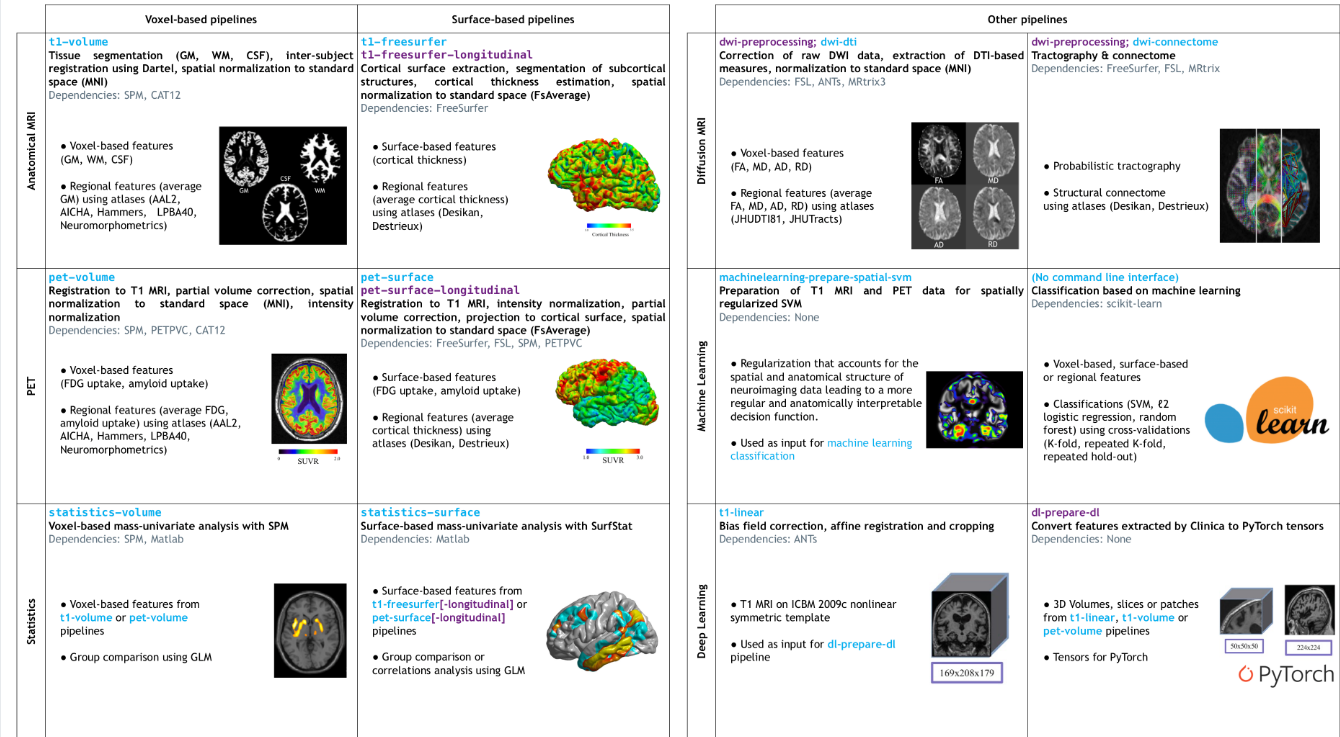
=> 기존에 진행하였던 방법이 Voxel-based features를 활용한 방법이다.
Result
Experiment Setting
- Train Dataset: ADNI
- Validation Dataset: ADNI
- Test Dataset: ADNI, AIBL, OASIS
- 5 Cross Validation
위에서 지적한 Data Leakage를 모두 만족할 수 있도록 구성하였고, Metric또한 Unbalanced한 Subject를 위하여 Balanced Accuracy, ROI, AUC로서 평가하였다.
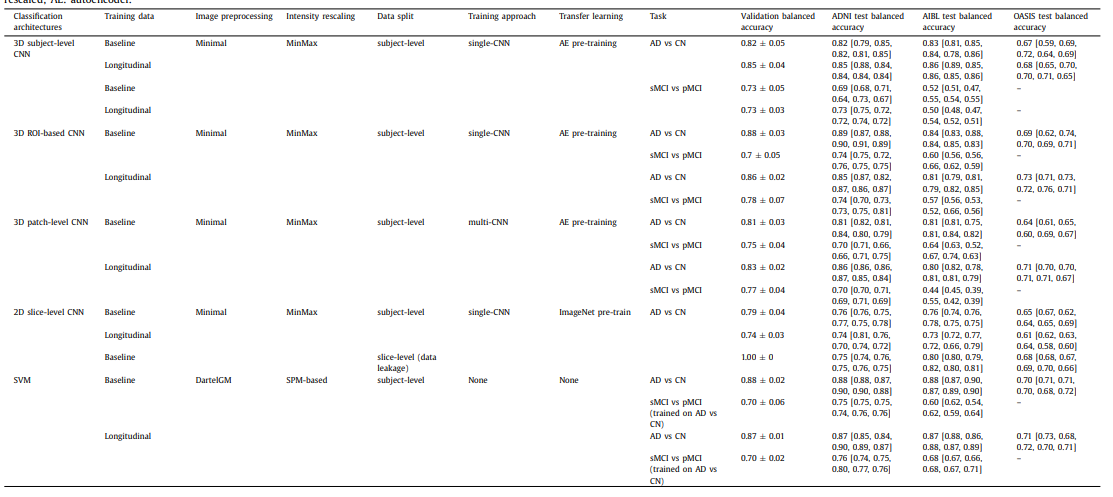
Experiment Result
Discussion
Overall, a major result of the present paper is that, with the sample size which is available in ADNI, CNNs did not provide an increase in performance compared to SVM.
Unbiased evaluation of the performance is an essential task in ML. This is particularly critical for DL because of the extreme flexibility of the models and of the numerous architecture and training hyperparameters that can be chosen. In particular, it is crucial that such choices are not made using the test set. We chose a very strict validation strategy in that respect: the test sets were left untouched until the end of the peer-review process. This guarantees that only the final models, after all possible adjustments, are carried to the test set. Moreover, it is important to assess generalization not only to unseen subjects but also to other studies in which image acquisitions or patient inclusion criteria can vary. In the present paper, we used three test sets from the ADNI, AIBL and OASIS databases to assess different generalization aspects.
중요하게 생각할 수 있는 결과는 다음과 같다.
- Voxel-based feature를 사용한 SVM은 다른 DeepLearning방법인 CNN보다 비슷하거나 더 높은 성향을 보인다.
- ADNI로 Train -> Test할 시에 비슷한 성능을 보이고, 다른 Dataset에 Model을 적용하였을 때는 더 좋은 Performance를 보여준다.
- BaseLine과 Longitudinal의 차이가 거의 없다.

Leave a comment