Paper25. Uncertainty-Guided Progressive GANs for Medical Image Translation
Uncertainty-Guided Progressive GANs for Medical Image Translation
출처: Uncertainty-Guided Progressive GANs for Medical Image Translation
코드: UncerGuidedI2I GitHub
Abstract
Image-to-image translation plays a vital role in tackling various medical imaging tasks such as attenuation correction, motion correction, undersampled reconstruction, and denoising. Generative adversarial networks have been shown to achieve the state-of-the-art in generating high fidelity images for these tasks. However, the state-of-the-art GANbased frameworks do not estimate the uncertainty in the predictions made by the network that is essential for making informed medical decisions and subsequent revision by medical experts and has recently been shown to improve the performance and interpretability of the model. In this work, we propose an uncertainty-guided progressive learning scheme for image-to-image translation. By incorporating aleatoric uncertainty as attention maps for GANs trained in a progressive manner, we generate images of increasing fidelity progressively. We demonstrate the efficacy of our model on three challenging medical image translation tasks, including PET to CT translation, undersampled MRI reconstruction, and MRI motion artefact correction. Our model generalizes well in three different tasks and improves performance over state of the art under fullsupervision and weak-supervision with limited data. Code is released here: https://github.com/ExplainableML/UncerGuidedI2I
이 논문의 Contribution은 “일반적인 GAN처럼 iamge-to-image translation을 진행한다. 하지만, 추가적으로 Attention map으로서 uncertainty으로서 가중치를 주고, 이러한 input을 사용하여 점진적으로 model의 fidelity를 증가시킨다. (uncertainty를 줄인다.)”
Introduction
Further examples are related to image reconstruction and/or correction in MRI: Reconstruction of undisturbed artifact-free images is hard to achieve with traditional methods; deep-learning-based image-to-image translation can solve this challenge. In particular, generative adversarial networks (GAN) based on convolutional neural networks (CNN) have proven to provide a high visual quality of the generated synthetic images. However, predictions of GANs can be unreliable, and particularly in medical applications, the quantification of uncertainty is of high importance for the interpretation of the results. In this work, we propose a generic end-to-end model that introduces high-capacity conditional progressive GANs to synthesize high-quality images, using aleatoric uncertainty estimates as the guide to focus on improving image quality in regions where the network is highly uncertain about the prediction.
개인적으로 해당 논문에서 Contribution이라고 생각하는 부분이다. 의료분야에서 image-to-image translation으로서 서로 다른 modality의 image를 생성하는 일은 매우 중요한 일이다. 하지만, 이러한 image를 생성하는 과정에서 신뢰할 수 있는 image를 생성한다는 것은 의료 분야에서 매우 중요한 문제이다. 따라서 해당 논문에서는 image를 생성할 뿐만 아니라 생성된 image에 대하여 uncertainty를 보여주므로 인하여 어느정도 신뢰할 수 image인지 보여준다.
Uncertainty-Guided Progressive GAN (UP-GAN)
Notation
- A, B: Two image domains with a set of images $S_A:={a_1, a_2, \ldots, a_n}$ and $S_B:={b_1, b_2, \ldots, b_n}$
- $a_i, b_i$: i-th image from domain A and B
- $P_{AB}$: Unknown probability distribution with K pixels (i.e. $(a_i, b_i) \sim P_{AB} \forall i$)
- $u_{ik}$: $k^{th}$ pixel of a particular image $u_i$
- $g(\cdot; \theta_i)_i$: i-th generator with $\theta_i$ parameters
- $D(\cdot; \phi_i)_i$: i-th patch discriminator with $\phi_i$ parameters
Uncertainty-Guided Progressive GAN (UP-GAN) Workflow
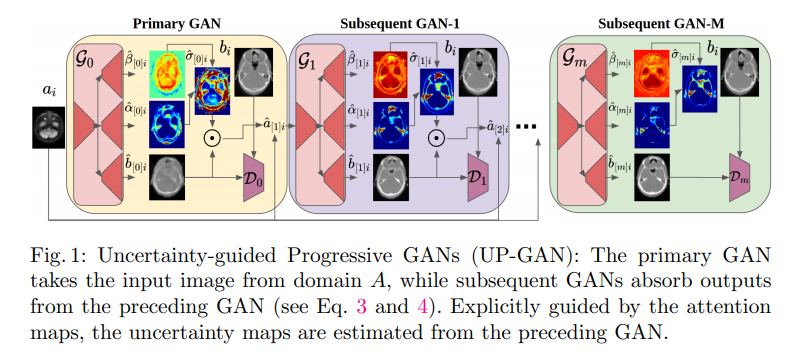
위와 같이 Notation이 주어졌을 때, GAN의 목적은 ${(a_i, b_i)}$가 주어졌을 경우 $P_{B|A}$를 학습하여 $P_{AB}$에 따라 A -> B로서 mapping하는 것 이다.
$a_i$가 주어졌을 경우, \(\hat{b}_{i}\)를 예측하는 GAN model을 사용하게 되면, pixel wise error는 \(\epsilon_{ij} = \hat{b}_{ij} - b_{ij}\)이다.
해당 논문은 위와같이 i.i.d 라고 가정하지 않고, ‘modelling the residual as non i.i.d variables and learning the
optimal distribution from the dataset’ 하는 새로운 방법을 제시한다.
Figure 1을 살펴보게 되면 제안하는 GAN model은 ‘cascaded GNAs’ 로서 이루워져 있고 ‘aleatoric uncertainty’를 측정할 수 있다. 해당 model은 scale ($\alpha$), shape ($\beta$)을 학습하게 되며, \(\epsilon_{ij} = \hat{b}_{ij} - b_{ij}\)이고, error가 zero-mean generalized Gaussian distribution (GCD)라 가정하면, error는 아래와 같이 측정할 수 있다. \(\epsilon_{ij} \sim \text{GCD}(\epsilon;0, \alpha_{ij}, \beta_{ij}) \equiv \beta_{ij} (2\alpha_{ij} \Gamma (\beta_{ij}^{-1})) \text{exp} (-\alpha_{ij}^{-1} | \epsilon |^{\beta_{ij}})\) 개인적으로 이해한 위의 식의 의미는 Figure 1과 대입하여 생각하였을때, Error가 큰 이유는 Uncertainty가 크다는 이유이고 이러한 이유는 (1) Uncertainty가 있는 부분이 많거나 (shape-$\alpha$), (2) 해당 부위의 Uncertainty가 커서 (scale-$\beta$) 이다. 해당 논문은 이러한 Uncertainty를 측정($\sigma$)하여 attention map으로 사용하고, 이러한 attention을 고려하여 새로운 input으로서 sequence하게 들어가도록 구성하였다. 해당 Model은 아래와 같이 구성되고 학습될 수 있다.
Primary GAN.
첫번째 GAN으로서 i.i.d라고 가정하였을때, 일반적인 GAN과 동일한 Network이다. 해당 model은 pix2pix와 마찬가지로 일반적인 GAN의 형태인 generator로서 U-Net을 사용하였고, Discriminator로서 Patch discriminator를 사용하였다. 위에서 정의한 (\(\hat{\alpha}_{[0]i}, \hat{\beta}_{[0]i}, \hat{b}_{[0]i}\))가 주어졌을때의 기본적인 GAN의 Loss형태로 나타내면 Generator Loss (\(L_{\alpha \beta}^{G}\))와 Discriminator Loss(=Adversarial Loss, \(L_{adv}^{D}\))는 아래와 같이 나타낼 수 있다. (generator의 Loss가 이해되지 않으면 GAN description참조.)
- \(L_{\alpha \beta}^G (\hat{\alpha}_{[0]i}, \hat{\beta}_{[0]i}, \hat{b}_{[0]i}, b_i) = \frac{1}{K} \sum_{j}(\frac{|\hat{b}_{[0]ij} - b_{ij}|}{\hat{\alpha}_{[0]ij}})^{\hat{\beta}_{[0]ij}} - \text{log}\frac{\hat{\beta}_{[0]ij}}{\hat{\alpha}_{[0]ij}} + \text{log} \Gamma(\hat{\beta}_{[0]ij}^{-1})\)
- $L_{adv}^G = L_2(D_1(\hat{b}_{[0]i}), 1)$
- Loss for generator: $L_{tot}^G = \lambda_1 L_{\alpha \beta}^G + \lambda_2 L_{adv}^G$
- Loss for discriminator: $L_{adv}^{D} = L_2(D^A(b_i), 1) + L_2(D^A(\hat{b}_{[0]i}), 0)$
Subsequent GANs.
첫번째 GAN을 제외하고 이어지는 GAN의 Input은 아래와 같이 나타낼 수 있다.
- \(\hat{\sigma}_{[m-1]i} = \hat{\alpha}_{[m-1]i}\sqrt{\frac{\Gamma(3/\hat{\beta}_{[m-1]i})}{\Gamma(1/\hat{\beta}_{[m-1]i})}}\)
- \(f_{[m]i} = \hat{b}_{[m-1]i} \odot \frac{\hat{\sigma}_{[m-1]i}}{\sum_j \hat{\sigma }_{[m-1]ij}}\)
- $a_{[m]i} = \text{concat}(f_{[m]i}, a_i)$
위의 식을 살펴보게 되면 3가지 과정으로 이루워진다.
- GCA의 Standard deviation($\hat{\sigma}_{[m-1]i}$)을 곱하여 uncertanity를 사용한다.
- 1에서 구한 uncertanity를 attention map으로서 사용하여 기존의 prediction에 곱하여$f_{[m]i}$를 구한다.
- Original Input과 2에서 구한 값을 concat하여 새로운 input ($a_{[m]i}$)으로서 사용한다.
위의 식의 의미는 Standard Deviation이 클수록 Uncertainty가 크다는 것이다.
여기에서 다시 \(L_{\alpha \beta}^G (\hat{\alpha}_{[0]i}, \hat{\beta}_{[0]i}, \hat{b}_{[0]i}, b_i)\)의 식을 3개의 Term으로서 나누어서 생각해보자
- Term 1: \(\frac{1}{K} \sum_{j}(\frac{|\hat{b}_{[0]ij} - b_{ij}|}{\hat{\alpha}_{[0]ij}})^{\hat{\beta}_{[0]ij}}\)
- Term 2: $\text{log} \hat{\alpha}_{[0]ij}$
- Term 3: \(\text{log} \Gamma(\hat{\beta}_{[0]ij}^{-1}) - \text{log}\hat{\beta}_{[0]ij}\)
Term 1은 Error인 \(|\hat{b}_{[0]ij} - b_{ij}|\)이 작아질 수록, Term 2, 3은 \(\alpha, \beta\)의 값이 작아질 수록 Loss의 값은 작아진다.
즉, 해당 Model은 GCD의 Standard deviation을 scale ($\alpha$), shape ($\beta$)로서 표현하여 Uncertanity를 얻어내고, Model의 학습은 Error와 Uncertanity가 작아지도록 학습된다.
Progressive training scheme.
해당 모델의 parameter initialization은 다음과 같은 과정으로 이루워진다.
- Initialize $\theta_1, \phi_1$ using the training set ($S_A, S_B$) to minimize the loss function given by $L_{tot}^G, L_{adv}^D$
- For the suubsequent GANs, we initialize the $\theta_m \cup \phi_m (m>1)$ by fixing the weights of all the previous generators and training the $m^{th}$ GAN alone.
- Once all the parameters have been initialized, we do further fine tuning by training all the networks end-to-end by combining the loss functions of all the intermediate phasese and a significantly smaller learning-rate.
Code를 정확히 봐야 이해하겠지만, 각각의 GAN을 1-to-m까지 훈련 한다. 다음순서의 GAN은 이전 GAN의 parameters는 Fix시키며 Attention map을 가져와서 학습을 진행한다. 모든 훈련된 GAN은 연결하여 end-to-end로서 훈련을 진행하게 된다.
해당 Training과정에서 각각의 GAN의 Hyperparmeter를 아래와 같이 Setting하였다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
list_epochs = [50, 50, 150]
list_lambda1 = [1, 0.5, 0.1]
list_lambda2 = [0.0001, 0.001, 0.01]
for num_epochs, lam1, lam2 in zip(list_epochs, list_lambda1, list_lambda2):
...
total_loss = lam1*F.l1_loss(rec_B, xB) + lam2*bayeGen_loss(rec_B, rec_alpha_B, rec_beta_B, xB)
위에서 total loss는 \(L_{\alpha \beta}^G (\hat{\alpha}_{[0]i}, \hat{\beta}_{[0]i}, \hat{b}_{[0]i}, b_i)\)을 의미한다. 즉, 해당 논문의 model은 처음에는 labmda2의 값을 매우 낮추어서, 기존 GAN과 동일한 효과를 얻으려 하였고, 점차적으로 GAN을 지날수록 Uncertainty인 부분을 강조하여 학습한다. 이러한 결과로서 GAN은 기존에 잘 되었던 부분보다, Uncertainty높았던 학습이 잘 되지 않았던 부분들어 대하여 specific하게 학습할 수 있다.
참조
Experiments
- PET to CT translation: CT image from PET scans to CT(Siemens Biograph mCR) // Train: 29, Val: 5, Test: 15
- Undersampled MRI reconstruction // Train: 200, Val: 100, Test: 200
- MRI Motion correction (Dataset is equal to 2 Experiemnts)
Visualization
Quantitative results in the presence of limited labeled training data.
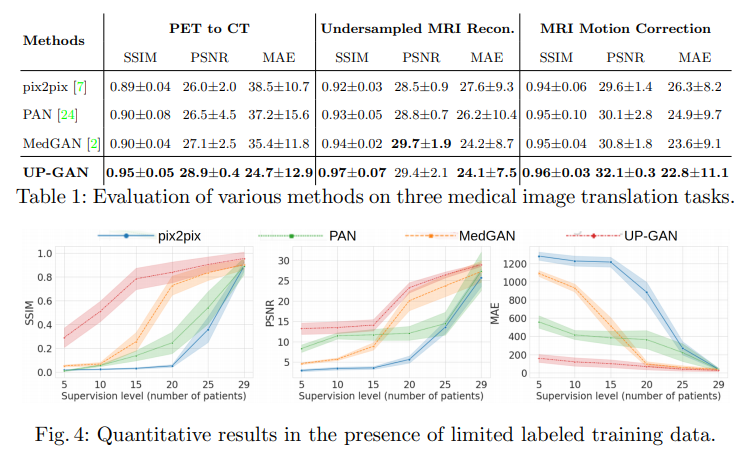
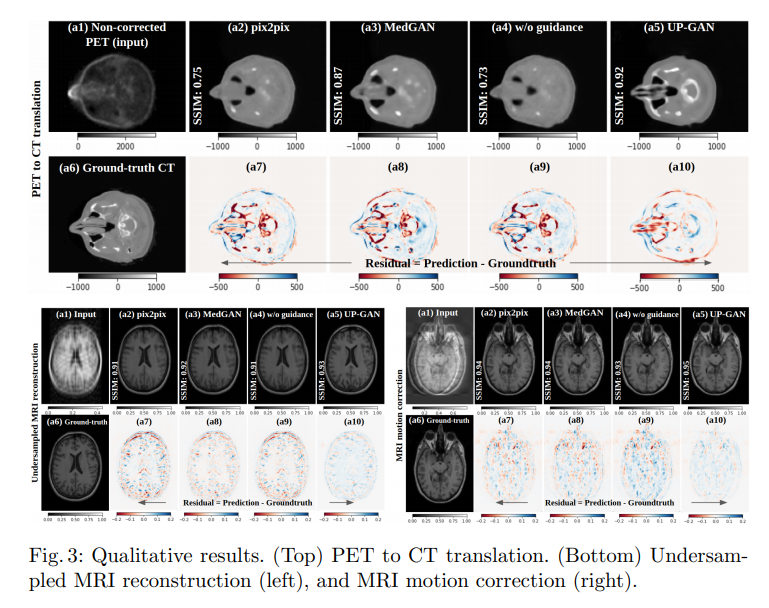
위의 Experiments의 결과를 살펴보게 되면, 모든 Experiemnts에서 compared methods (pix2pix, MedGAN, w/o guidance)보다 제안하는 UP-GAN에서 결과가 좋은 것을 살펴볼 수 있다. 특히 Dataset이 적을수록 다른 compared Methods에 비하여 성능이 좋은 것을 알 수 있다.
Conclusion
해당 논문은 Uncertainty를 attention map으로서 강조하여 sequence한 model에 넣어 점점 더 reconstruction을 잘하는 UP-GAN을 제안한다. 특히, sample의 수가 적을수록 다른 compared models에 비하여 차이가 큰 것을 알 수 있다. 하지만, sample의 수가 많아지면 많아질수록 기존의 model들과 성능이 비슷해 지는 것을 알 수 있다.

Leave a comment