DataAnalysis-분류분석
분류(Classfication)
소속 집단을 알고 있는 데이터를 이용하여 모형을 만들어서 소속집단을 모르는 데이터들의 집단을 결정하는 기법
Supervised Learning.
- 로지스틱 회귀(Logistic regression)
- 의사결정 나무(Decision Tree)
- 랜덤 포레스트(Random Forest)
- 나이브베이즈 분류(Naive Bayes Classification)
- SVM(Support Vector Machine)
- K-NN Classfication
위에대한 자세한 내용은 아래 링크 참조
분류분석 자세한 내용
공통사항
많은 분류분석을 비교하기 전에 공통적으로 사용하는 것을 Method로서 선언하였다.
Data 는 Iris Data중 Sepal length, Sepal width를 사용하였다.
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split를 활용하여 전체 Data중에서 30%는 Test, 70%는 Train으로서 사용하였다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
#Iris Data 불러오기
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data[:, :2]
Y = iris.target
#Train, Test DataSet분리
train_x, test_x, train_y ,test_y = train_test_split(X,Y, test_size = 0.3, random_state=0)
정확도를 측정하는 Method는 Parameter로서 예상값, 실제값, Train or Test인지 알려주는 String parameter을 받아 정확도를 측정하게 된다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
#정확도 측정 Method
def accuracy(X,Y,S):
total = len(X)
count = 0
for i in range(1,len(X)):
if(X[i] == Y[i]):
count = count+1
print(S,'정확도는 ',round(count/total,4)*100,'% 입니다')
시각화를 하는 Method는 실제 Data의 분포와 이것을 어떻게 분리했는지를 나타내주는 Method이다.
아래 코드는 다음을 참조하여서 작성하였다.
시각화 코드 참조 사이트
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
#시각화 Method
def visualization(model):
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - .5, X[:, 0].max() + .5
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - .5, X[:, 1].max() + .5
h = .02 # step size in the mesh
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
Z = model.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
# Put the result into a color plot
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.figure(1, figsize=(4, 3))
plt.pcolormesh(xx, yy, Z, cmap=plt.cm.Paired)
# Plot also the training points
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=Y, edgecolors='k', cmap=plt.cm.Paired)
plt.xlabel('Sepal length')
plt.ylabel('Sepal width')
plt.xlim(xx.min(), xx.max())
plt.ylim(yy.min(), yy.max())
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.show()
로지스틱 회귀(Logistic regression)
로지스틱 회귀는 다음과 같은 code를 import하여 사용할 수 있다.
1
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
로지스틱 회귀 구현
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
#Logistic Regression
logreg = LogisticRegression(C=1e5, solver='lbfgs', multi_class='multinomial')
# Create an instance of Logistic Regression Classifier and fit the data.
logreg.fit(train_x, train_y)
#Traing 정확도
accuracy(train_y,logreg.predict(train_x),'Train ')
#Test 정확도
accuracy(test_y,logreg.predict(test_x),'Test ')
#시각화
visualization(logreg)
Train 정확도는 82.86 % 입니다
Test 정확도는 80.0 % 입니다
로지스틱 회귀 시각화
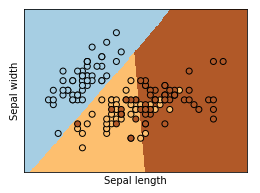
의사결정 나무(Decision Tree)
의사결정 나무는 다음과 같은 code를 import하여 사용할 수 있다.
1
from sklearn import tree
의사결정 나무 구현
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
#Decision Tree
import pydotplus
from sklearn import tree
DecisionTree = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion= "entropy", max_depth=3)
DecisionTree.fit(train_x, train_y)
#Traing 정확도
accuracy(train_y,DecisionTree.predict(train_x),'Train ')
#Test 정확도
accuracy(test_y,DecisionTree.predict(test_x),'Test ')
#시각화
visualization(DecisionTree)
Train 정확도는 81.89999999999999 % 입니다
Test 정확도는 66.67 % 입니다
의사결정 나무 시각화1
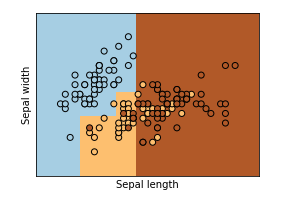
의사결정 나무 시각화2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
#Decision Treee 시각화
from matplotlib.pyplot import imread
import graphviz
label_names=['Sepal length','Sepal width']
dot_data = tree.export_graphviz(DecisionTree, feature_names=label_names,
out_file='tree.dot',class_names=["0","1","2"], filled=True, rounded=True)
with open("tree.dot") as f:
dot_graph = f.read()
display(graphviz.Source(dot_graph))
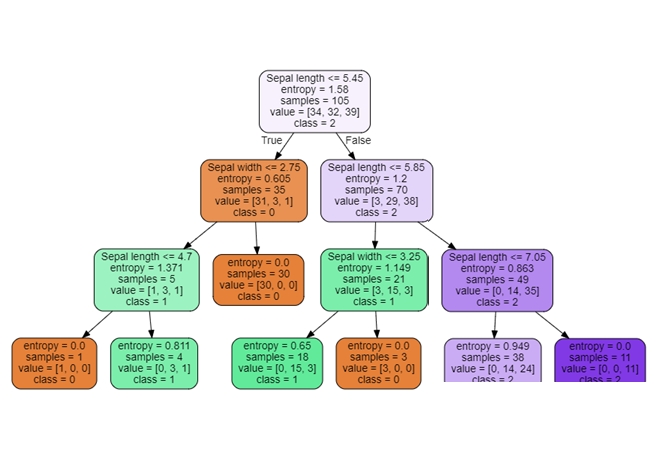
의사결정 나무 중요도 시각화
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
#Decision Treee 중요도 시각화
def plot_feature_importances(model):
plt.barh(range(2), model.feature_importances_, align='center')
plt.yticks(np.arange(2), ['Sepal length','Sepal width'])
plt.xlabel("Feature Importance Percent")
plt.ylabel("Feature")
plt.ylim(-1, 2)
plot_feature_importances(DecisionTree)
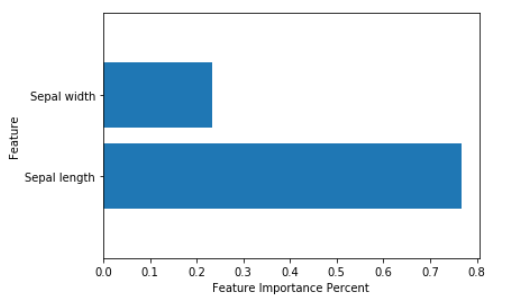
랜덤포레스트(Random Forest)
랜덤포레스트는 다음과 같은 code를 import하여 사용할 수 있다.
1
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
랜덤포레스트 구현
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
#Random Forest
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
RandomForest = RandomForestClassifier(criterion = "entropy", n_estimators=10)
RandomForest.fit(train_x, train_y)
#Traing 정확도
accuracy(train_y,RandomForest.predict(train_x),'Train ')
#Test 정확도
accuracy(test_y,RandomForest.predict(test_x),'Test ')
#시각화
visualization(RandomForest)
Train 정확도는 91.43 % 입니다
Test 정확도는 66.67 % 입니다
랜덤포레스트 시각화
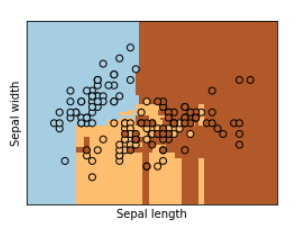
나이브베이즈 분류(Naive Bayes Classification)
나이브베이즈 분류는 다음과 같은 code를 import하여 사용할 수 있다.
1
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
나이브베이즈 분류 구현
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
#Naive Bayes Classification
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
NaiveBayes = GaussianNB().fit(train_x, train_y)
#Traing 정확도
accuracy(train_y,NaiveBayes.predict(train_x),'Train ')
#Test 정확도
accuracy(test_y,NaiveBayes.predict(test_x),'Test ')
#시각화
visualization(NaiveBayes)
Train 정확도는 80.0 % 입니다
Test 정확도는 80.0 % 입니다
나이브베이즈 분류 시각화
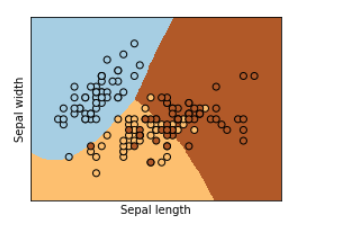
K-NN Classfication
K-NN Classfication는 다음과 같은 code를 import하여 사용할 수 있다.
1
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsRegressor
K-NN Classfication 구현
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
#K-NN
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsRegressor
KNN = KNeighborsRegressor(n_neighbors = 2, n_jobs = -1)
# n_jobs = -1 : "직접 판단하라는 의미"
KNN.fit(train_x, train_y)
#Traing 정확도
accuracy(train_y,KNN.predict(train_x),'Train ')
#Test 정확도
accuracy(test_y,KNN.predict(test_x),'Test ')
#시각화
visualization(KNN)
Train 정확도는 73.33 % 입니다
Test 정확도는 53.33 % 입니다
K-NN Classfication 시각화
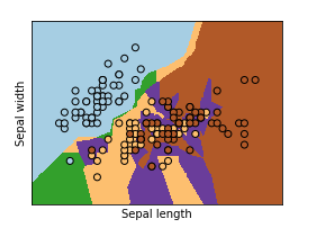
SVM(Support Vector Machine)
SVM는 다음과 같은 code를 import하여 사용할 수 있다.
1
from sklearn import svm
SVM 구현
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
#SVM
from sklearn import svm
SVM = svm.LinearSVC(C=10)
SVM.fit(train_x, train_y)
#Traing 정확도
accuracy(train_y,SVM.predict(train_x),'Train ')
#Test 정확도
accuracy(test_y,SVM.predict(test_x),'Test ')
#시각화
visualization(SVM)
Train 정확도는 80.95 % 입니다
Test 정확도는 80.0 % 입니다
SVM 시각화
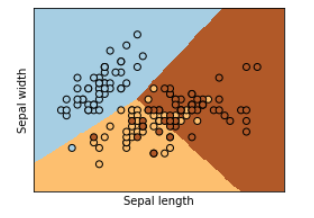
최종결과
| 방법 | 정확도 |
| Logistic Regression |
|
| Decision Tree |
|
| Random Forest |
|
| Naive Bayes Classification |
|
| K-NN |
|
| SVM |
|
위의 결과표를 참조하면 SVM, Logistic Regression, Naive Bayes Classification이 가장 적절한 Model이라는 것을 판단할 수 있다.
하지만 위에서의 Code는 조정 가능한 Parameter를 바꿔가면서 비교한 것이 아니다.
실제 Model을 만들고 적용할 떄는 조정 가능한 Parameter를 조정해가면서 최적의 Model을 찾는 것이 필요하다.
잠조: 원본코드
코드에 문제가 있거나 궁금한 점이 있으면 wjddyd66@naver.com으로 Mail을 남겨주세요.

Leave a comment