Paper09. PALLADIO
PALLADIO: a parallel framework for robust variable selection in high-dimensional data
PALLADIO: a parallel framework for robust variable selection in high-dimensional data
(https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7836840)
Abstract
The main goal of supervised data analytics is to model a target phenomenon given a limited amount of samples, each represented by an arbitrarily large number of variables. Especially when the number of variables is much larger than the number of available samples, variable selection is a key step as it allows to identify a possibly reduced subset of relevant variables describing the observed phenomenon. Obtaining interpretable and reliable results, in this highly indeterminate scenario, is often a non-trivial task. In this work we present PALLADIO, a framework designed for HPC cluster architectures, that is able to provide robust variable selection in high-dimensional problems. PALLADIO is developed in Python and it integrates CUDA kernels to decrease the computational time needed for several independent element-wise operations. The scalability of the proposed framework is assessed on synthetic data of different sizes, which represent realistic scenarios.
- 해당논문에서 주장하는 Model은 Sample보다 Dimension이 큰 Dataset에 대하여 Feature Selection을 Robust하게 뽑아낼 수 있는 Model을 제안
- 이러한 Model을 HPC Cluster Architecture + CUDA를 지원함으로서 빠르게 수행될 수 있는 Python Package로서 제공
Introduction
Introduction에서 강조하고 있는 것은 Abstract와 동일하다.
먼저, 많은 Statistical Model은 n(sample) » d(feature)인 경우에 적합하고 그 반대인 경우에는 curse of dimensionality로서 충분한 performance를 내지 못한다고 얘기하고 있다.
또한, High Dimension을 Feature Selection 하는 다른 방법(Lasso)의 경우에도, intuitive interpretation가 부족하다고 알려져있다.
해당 논문에서는 이러한 sample이 적고 intuitive interpretation이 가능한 Model로서 Permutation Test를 선택하였다.
하지만, Permutation Test는 일반적인 Statistical Model들에 비하여 많은 시간이 걸리게 되고, 이를 해결하기 위하여 HPC cluster architecture를 통하여 병렬처리를 하였다. Process간의 통신은 MPI로서 해결하고, Element Wise Operation을 위해서는 CUDA를 사용하여 처리 시간을 단축시켰다고 한다.
Background
Model Step은 다음과 같이 진행됩니다.
- Feature Selection
- Feature Selection으로 Feature로서 Prediction Model을 Train
- 해당 Model을 Testset으로서 Performance확인
Supervised Learning Setting
$$f: X \rightarrow y$$
$$y = X\beta + \epsilon, (\epsilon \text{: Noise } \beta: \text{: Weight})$$
- \(X \subseteq R^d\): Input: nxd
- \(y \subseteq R\): Output: nx1
Variable Selection
모든 Feature(\(\beta\))가 X와y사이의 관계가 있는 것이 아니고, 특정 Subset만 관련이 있다. 이러한 Subset을 뽑기위하여 \(\beta\)를 Sparse하게 만들어야 하고, 이러한 방법으로서 Regularization이 있다.
Regularization
$$L(y, f_{\beta}(X))(\text{Loss Function}) + \gamma \Omega(f_{\beta})(\text{Regularization})$$
\(\gamma\)는 Bias-Variance Tradeoff를 조절하는 Hyperparameter이다.
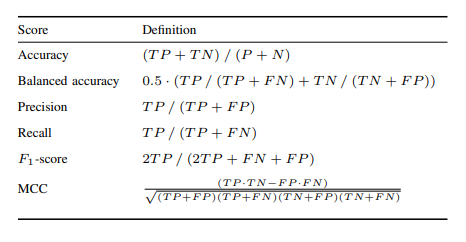
Performance Metric
Resampling Strategies
The validation of a learning machine can be done by estimating its generalization error, that is a measure of the level of prediction accuracy we expect the model to reach on previously unseen data.
Machine Learning에서 반드시 지켜야 하는 것을 잘 설명하고 있다. Test Data의 Label정보는 전혀 이용하지 않고, Generalization을 위하여 Validation Data를 사용한다. 이러한 Generalization을 증가시키기 위하여 MCCV(Monte Carlo Cross Validation)과 KCV(K-fold Cross Validation)이 가장 유명한 2가지의 Cross Validation의 종류이며, PALLADIO에서는 MCCV, KCV 둘 다 사용한다.
PALLADIO
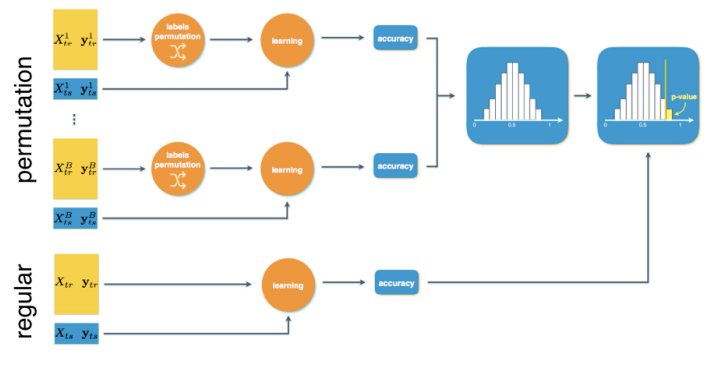
PALLADIO의 Framework이다. Dataset이 적은경우를 대비하여, Label을 섞어서 Random한 경우의 Performance를 여러번 섞어서 수행한다. 따라서 Permutation test를 진행하게 되고, 실제 Data를 적용시킨 Model을 Wilcoxon signed-rank test을 통하여 유의미한 Model인지 진행된다. PALLADIO의 step은 다음과 같다.
- MCCV로서 여러 experiment를 만들게 된다. Random Variabel은 pseudo-random number generator로서 생성이 된다.
- Parameter를 선택하기 위하여 KCV를 통하여 Grid Search를 수행하게 된다.
- 찾아낸 Model에 대하여 Permutation을 통하여 유의미한 Model인지 파악하게 된다.
2의 과정에서는 \(l_1l_2\)-Penalized regularization with double optimization이 수행된다.
\(l_1l_2\)-Penalized regularization with double optimization
PALLADIO은 n«d인 경우에 Feature 를 줄이기 위하여 사용된다.
위에서는 Resampling을 통하여 Generalization한 Model을 Selection하는 시도였다.
Model자체에서 Feature를 줄이기 위해서는 \(l_1l_2\) Penalization을 수행하게 된다.
$$\frac{1}{n}\| y-X\beta\|_2^2 + \mu \|\beta\|_2^2 + \gamma \|\beta\|_1$$
\(\beta, \gamma\)는 Regularization Term으로서 Hyperparameter로서 진행되며, 위에서 설명한 2번 Step처럼 KCV를 통한 Grid search로서 찾게 된다.
Usage
PALLADIO는 http://slipguru.github.io/palladio/ 링크에 Example과 Download Link가 담겨있다.
간단한 사용방법은 다음과 같다.
-
Data: d1 x n (d1: Feature, n: Sample), Label: n x 1로서 정의한다. Data의 column값과 Label의 Index값이 같아야 한다.
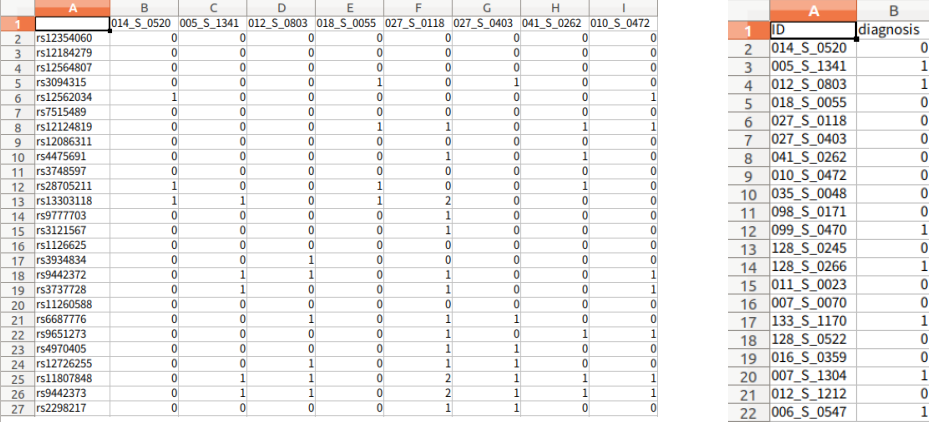
-
Config.py를 작성한다. => Config에서는 Experiment에서 사용할 Model를 설정할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
# Configuration file example for PALLADIO
# version: 2.0
import numpy as np
from sklearn.feature_selection import RFE
from sklearn.linear_model import SGDClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from palladio import datasets
import os
#####################
# DATASET PATHS ###
#####################
# * All the path are w.r.t. config file path
# The list of all files required for the experiments
data_path = 'value.csv'
target_path = 'label.csv'
# pandas.read_csv options
data_loading_options = {
'delimiter': ',',
'header': 0,
'index_col': 0
}
target_loading_options = data_loading_options
dataset = datasets.load_csv(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__),data_path),
os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__),target_path),
data_loading_options=data_loading_options,
target_loading_options=target_loading_options,
samples_on='col')
data, labels = dataset.data, dataset.target
feature_names = dataset.feature_names
#######################
# SESSION OPTIONS ###
#######################
session_folder = 'result'
# The learning task, if None palladio tries to guess it
# [see sklearn.utils.multiclass.type_of_target]
learning_task = None
# The number of repetitions of 'regular' experiments
n_splits_regular = 50
# The number of repetitions of 'permutation' experiments
n_splits_permutation = 50
#######################
# LEARNER OPTIONS ###
#######################
model = RFE(SGDClassifier(penalty='elasticnet', max_iter=1000, tol=1e-3), step=0.3)
# Set the estimator to be a GridSearchCV
param_grid = {
'n_features_to_select': [100, 200, 300],
'estimator__l1_ratio': np.logspace(-4, 0, 5),
}
estimator = GridSearchCV(model, param_grid=param_grid, cv=3, scoring='accuracy', n_jobs=1, iid=True)
# Set options for ModelAssessment
ma_options = {
'test_size': 0.25,
'scoring': 'accuracy',
'n_jobs': 40,
'n_splits': n_splits_regular
}
# For the Pipeline object, indicate the name of the step from which to
# retrieve the list of selected features
# For a single estimator which has a `coef_` attributes (e.g., elastic net or
# lasso) set to True
vs_analysis = True
# ~~ Signature Parameters
# ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
frequency_threshold = 0.7
# ~~ Plotting Options
# ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
score_surfaces_options = {
'logspace': ['estimator__C'],
'plot_errors': True
}
-
PALLADO에서 제공하는 pd_run.py를 수행
-
Output Directory를 기준으로 PALLADO에서 제공하는 pd_analysis.py를 수행
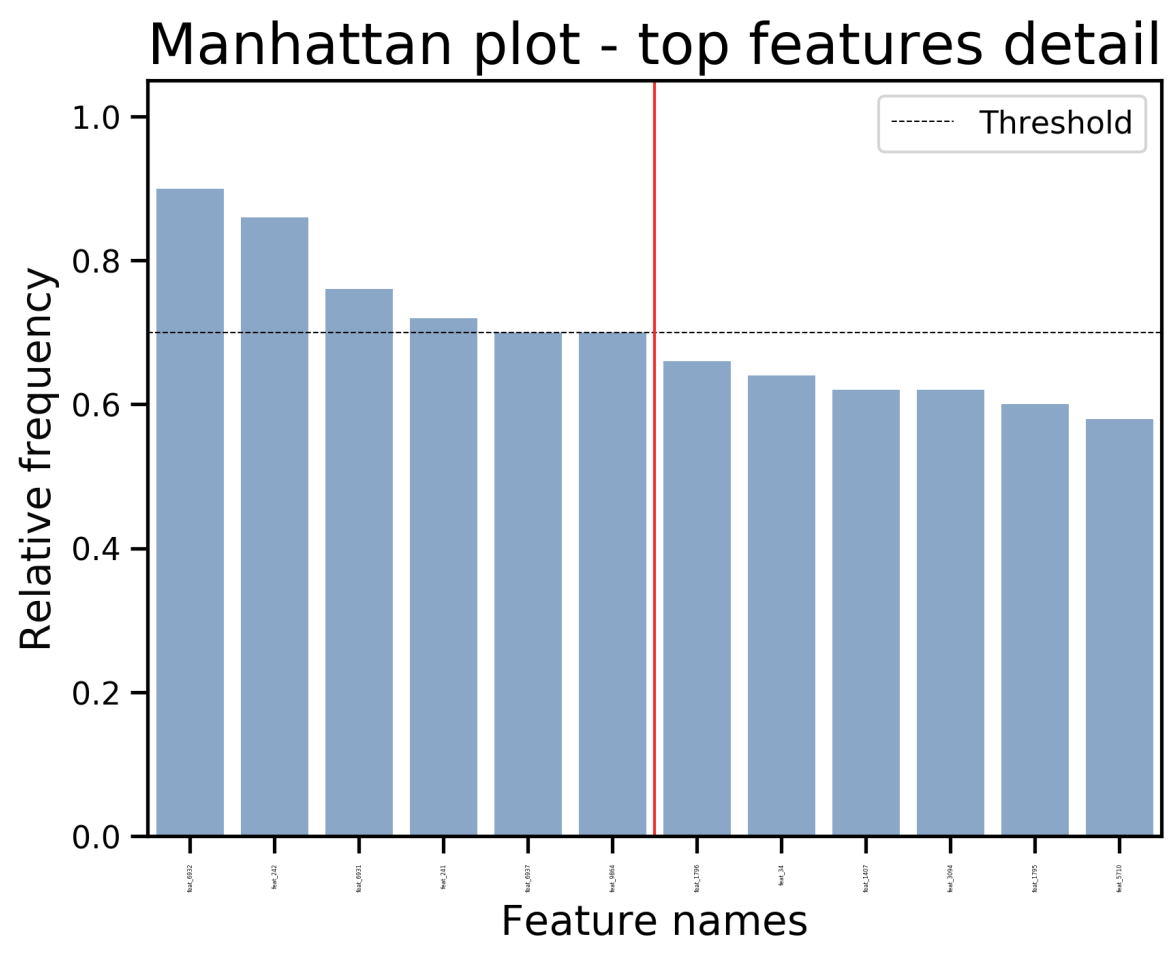
실제 결과를 보게 되면 다음과 같다.
Permutation Test에서 나온 Feature를 Select한 Count File => signature_permutation.txt
========================================
feat_3106 : 18.0
feat_9130 : 18.0
feat_8585 : 16.0
feat_445 : 16.0
feat_6948 : 16.0
feat_2099 : 16.0
feat_3313 : 16.0
feat_7267 : 14.0
...
Regular Test에서 나온 Feature를 Select한 Count File => signature_regular.txt
feat_6932 : 90.0
feat_242 : 86.0
feat_6931 : 76.0
feat_241 : 72.0
feat_9864 : 70.0
feat_6937 : 70.0
========================================
feat_1796 : 66.0
feat_34 : 64.0
feat_3094 : 62.0
feat_1407 : 62.0
feat_1795 : 60.0
feat_5710 : 58.0
feat_1506 : 56.0
...
Permutation과 Regular의 차이를 통해서 유의미한 p-value가 있는지 비교 => Accuracy, Balanced Accuracy, F1 Score, Recall, Precision의 결과 확인 가능
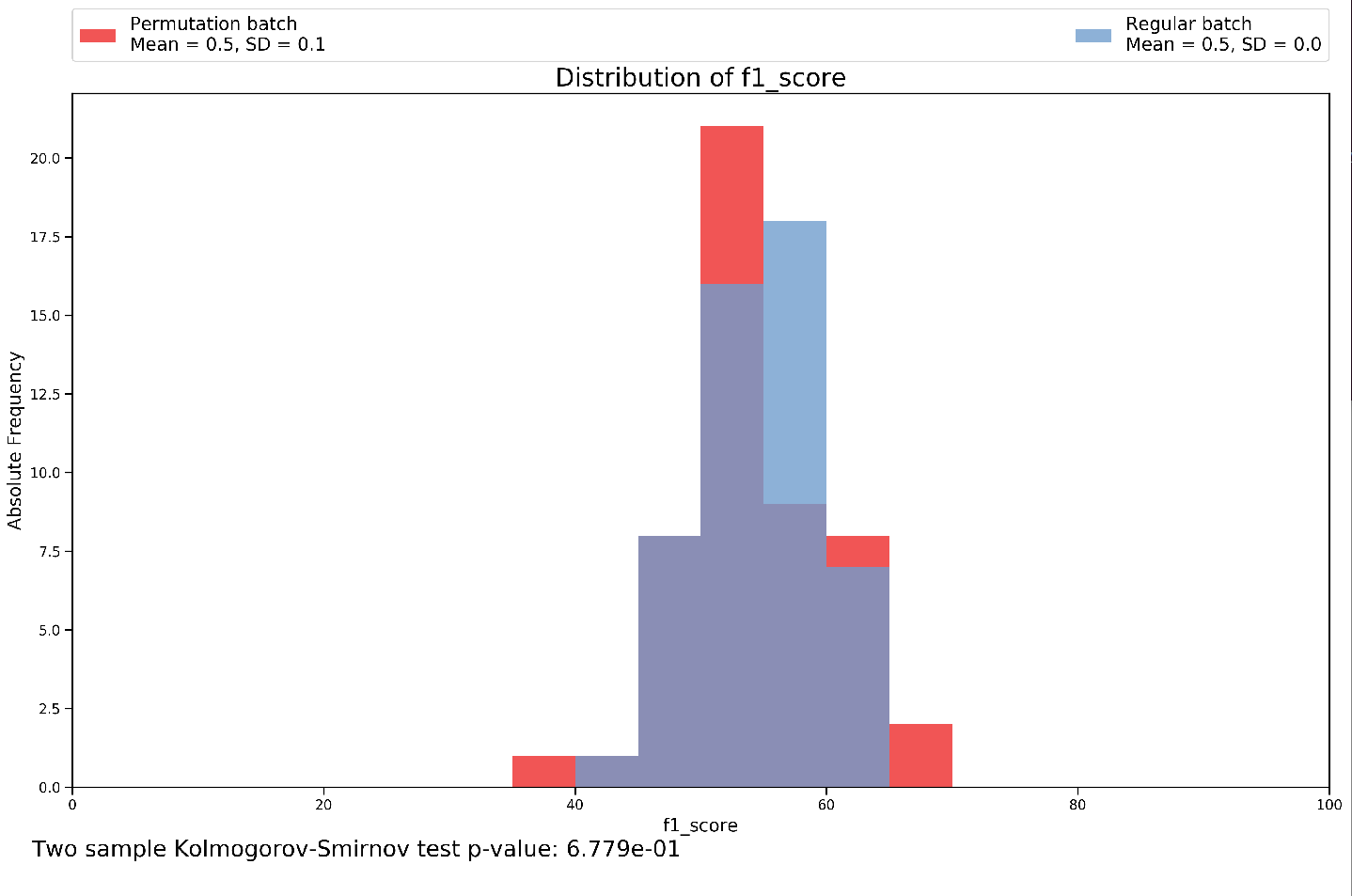
실제 Feature Frequency를 통하여 중요한 Feature Visualization

Leave a comment