Paper13. End-to-End Adversarial-Attention Network for Multi-Modal Clustering
End-to-End Adversarial-Attention Network for Multi-Modal Clustering
출처: End-to-End Adversarial-Attention Network for Multi-Modal Clustering
Abstract
Multi-modal clustering aims to cluster data into different groups by exploring complementary information from multiple modalities or views. Little work learns the deep fused representations of multiple modalities and simultaneously discovers the cluster structure with a discriminative loss. In this paper, we present an End-to-end Adversarial-attention network for Multi-modal Clustering (EAMC), where adversarial learning and attention mechanism are leveraged to align the latent feature distributions and quantify the importance of modalities respectively. To benefit from the joint training, we introduce a divergence-based clustering objective that not only encourages the separation and compactness of clusters but also enjoy a clear cluster structure by embedding the simplex geometry of the output space into the loss. The proposed network consists of modality-specific feature learning, modality fusion and cluster assignment three modules. It can be trained from scratch with batchmode based optimization and avoid an autoencoder pretraining stage. Comprehensive experiments conducted on five real-world datasets show the superiority and effectiveness of the proposed clustering method.
개인적으로 생각하는 이 논문의 Contribution은 다음과 같다.
- End-to-End로서 Multimodality Clustering을 할 수 있다. -> DeepCCA의 경우에는 Multimodality의 Correlation을 Maximize하는 형태로 학습하게 된다. 하지만, Training이 끝난 뒤, Clustering을 진행해양 하므로 End-to-End가 아니다.
- 서로 다른 Modality를 Fusion하는 과정에 있어서 Attention Layer를 통하여 각 Modality의 Importance를 다르게 지정할 수 있다.
- Modality Specific한 Latent Feature를 하나의 Fusion Latent Feature로 합치기 위하여 Adversial Network를 사용하여, Common Latent Feature을 훈련하려고 하였다.
Introduction
Although each modality has its own information and statistical properties, distinct modalities usually admit the same cluster structure. The rationale for using multi-modal data to learn the structured partition is that they can provide comprehensive estimation for the common pattern with the aid of the complementary information from modalities
개인적으로 Multi-Modal Data를 사용하는 이유라고 생각한다. 서로 다른 Modality로서 하나의 목적을 가지고 Model을 Training하게 되면, 해당 Task에 Comprehensive한 Information을 획득할 수 있다고 생각한다.
The mainstream research is to learn low-dimensional latent representations such that the mutual agreement of modalities can be reached in the latent space.
단순히 Concat하는 Eearly-Fusion의 방법은 performance가 좋지 않다는 것을 설명하고, 그로 인하여 Feature extractor를 거진 low-dimension인 latent representation로서 Fusion하는 방식으로서 연구가 진행되고 있다. 예를들어, CCA, MF, Kernel등이 있다. 또한 가장 큰 단점으로는 Linear한 방식으로서 Model이 학습되므로, Non-Linear한 표현을 할 수 없다는 것 이다.
Existing DNN-based multi-modal clustering methods fall into two categories.
이러한 문제를 해결하기 위하여 최신 연구들은 low-dimension-latent representation으로 나타내기 위한 Feature Extractor를 DNN을 사용하였고, 이렇나 방법은 크게 2가지가 존재하게 된다.
The first category regards multimodal feature learning and cluster assignment as separated processes.
DeepCCA의 예로서, End-to-End로서 학습할 수 없고, 서로 다른 Modality의 Correlation을 Maximization하게 학습한 뒤 K-Means로서 학습해야 하는 2 Step을 거쳐야 하는 단점이 발생하게 된다.
DAMC exemplifies this line of work. It works by pretraining multi-view autoencoder and then jointly optimizing the consensus cluster centroids, autoencoder networks and adversarial networks. Although DAMC has gained satisfactory results, it still faces some issues. On one hand, it equally treats each modality regardless of the quality difference among modalities, which makes it difficult to obtain optimal latent representations for clustering.
DAMC(Deep Adversarial Multi-view Clustering Network)는 End-to-End의 방법이지만, 각 Modality의 중요성을 동등하게 취급하므로, Clustering을 위한 최적의 latent representation으로서 나타내기 어렵다는 단점을 가지고 있다.
Through the adversarial process, modality invariance in the latent space can be reached more efficiently. Besides, we propose to quantify the importance of different modalities by introducing attention layer, which adaptively assigns the weight for each modality. Furthermore, we introduce a divergencebased clustering loss to guide the network training.
위에서 제시한 큰 3개의 문제점을 해결할 수 있는 Model을 현재 Paper에서는 주장한다.
- End-to-End Model -> Clustering loss를 Training과정에 포함시키는 1 Step Model
- 각 Modality의 Fusion -> Los latent representation을 Adversial Network를 통하여 Common한 latent representation 획득
- 각 Modality의 중요성 -> Attention Network를 통하여 각 Modality의 대한 중요도를 학습
해당 논문에서 제시하는 Model은 아래 그림과 같다.
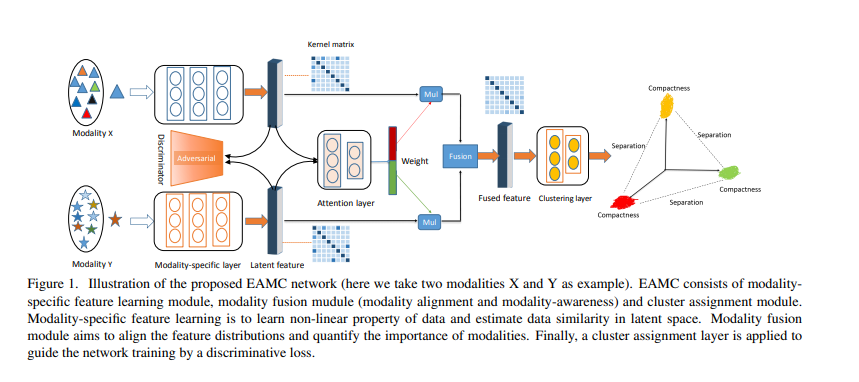
Proposed Model
Notation
- \(n\): Number of samples
- \(V\): Number of modalities
- \(d_v\): Dimension of \(v\) modality
- \(D = {X^{1}, \cdots X^{v}, \cdots, X^{V}}\): Dataset
- \(E_v (\cdot)\): Encoder of v modality
- \(\theta_e^v\): Parameter of \(E_v\)
- \(H^v = E_v(X^v;\theta_e^v)\):Encoder latent features
- \(K_{ij}^v = \text{exp}(-\|h_i^v - h_j^v\|_2/2\sigma^2)\): Gaussian Kernel
Network Architecture 위의 Figure1을 살펴보게 되면, 해당 논문에서 주장하는 Model은 크게 3가지로 나눌 수 있다.
- Modality-Specific Feature: 각각의 Modality의 specific한 특징을 얻어낼 수 있다.
- Modality Fusion: 서로 다른 Modality를 통하여 Comprehensive한 Information을 얻어낼 수 있다.
- Clustering: 1, 2를 활용하여 원래 목적인 Clustering을 실시하게 된다.
(A) Modality-Specific Feature Learning
Modality-Specific Feature Learning의 목적은 Input Data를 Low Dimension인 Latent representation으로서 나타내는 것 이다. 순서는 다음과 같다.
- Encoder의 Output(\(H^v = E_v(X^v;\theta_e^v)\))을 구한다.
- 각각의 Encoder의 Output(Decoder의 Input)을 i.i.d Gaussian Distribution으로서 나타내기 위하여 \(K_{ij}^v = \text{exp}(-\|h_i^v - h_j^v\|_2/2\sigma^2)\)을 구한다.
이전까지는 DNN의 weight에 Proior로서 Gaussian Distribution을 가정하는 L2 Regularization을 많이 사용하였다.
현재 수식을 살펴보면, Encoder의 Output(Decoder의 Input)또한 Gaussian Distribution으로서 나타내기 위하여 위와 같은 수식을 사용한다. Deep Neural Networks with Random Gaussian Weights: A Universal Classification Strategy?을 참고하면, Gaussian Weights의 장점이 나온다고 한다.
만약, Data의 sample의 수인 n이 크다고 가정하게 되면, VAE와 동일하다는 것을 알 수 있다.
(B) Modality Fusion
Modality Fusion에서 수행하는 목적은 크게 2가지이다.
- 각 Modality를 하나의 Comprehensive information을 가지고 있는 Matrix로서 나타내는 것을 목적으로 한다. 따라서, Adversial Network를 Discriminator로서 사용한다. EX) real data \(h_i^1 \in H^1\)이라고 가정하면, fake data는 \(h_j^1 \in H^j \text{ s.t. } j=2, \cdots,V\)로서 Discriminator의 Input에 넣게 된다. 점차적으로, 각 Modality의 Latent space는 동일하게 변할 것 이다.
- 각각의 Modality의 중요도를 학습하기 위하여 Attention Layer를 사용한다. Attention Layer의 식은 다음과 같다.
- \(h = [h^1, h^2, \cdots, h^V]\): Concat all latent representation
- \(\text{act = FCs}(h)\): 3 Fully connected layers
- \(e = \text{Softmax(sigmoid(act)}/\tau)\)
- \(w = \text{Mean}(e, \text{dim}=0)\): Attention Score
위와 같이 정의하게 되면, 최종적인 Cluster에 들어가는 Input은 다음과 같이 정의할 수 있다.
$$h_f = \sum_{v} w_v h^v$$
(C) Cluster Assignment
Cluster의 경우에는 Soft Cluster를 사용하였다고 나와있다.
Loss Function Loss Function같은 경우에도 크게 2가지로 나누어져 있다. Fusion Loss와 Clustering Loss이다. Modality-Specific Feature를 뽑아내는 Encoder는 이 2가지 Loss에 모두 영향을 받는다.
1) Fusion Loss
$$L_{adv} = \min_{\theta_e^v} \max_{\theta_d^v} \sum_{v=2}^V \mathbb{E}_{h^1 \text{~} p^1} [log D_v (h^1)] + \mathbb{E}_{h^v \text{~} p_v} [log(1-D_v(h^v))]$$
기본적으로 많이 사용하는 minmax adversial loss를 선택하였다. minmax adversial loss에 대한 자세한 내용은 아래 링크를 참조하다.
minmax adversial loss링크
또한 중요한 점은 모든 Modality의 Pair로서 선택하지 않았다는 것 이다. All possible combination의 경우의수는 \(2^V\)로서 많아지기 때문이다.
$$L_{att} = \|K^f - K^c\|_F^2$$
- \(K^f\): Fused features with Gaussian Kernel
- \(K^c = \sum_{v}w_v K^v\)
위의 Loss에 대한 효과는 다음과 같이 설명하고 있다.
The extra affect of (6) is that the weight is further considered in metric level such that the fused results are more reliable.
Deep Neural Networks with Random Gaussian Weights: A Universal Classification Strategy?을 읽어봐야 사용하는 자세한 이유를 알 수 있을 것 같습니다. 현재 상황으로는 각각의 Output에서 중요하다고 생각하는 것을 비슷하게 학습하기 위해서라고 생각하고 있습니다.
2) Clustering Loss
현재 논문에서는 Clustering Loss를 Cauchy-Schward divergence를 통한 새로운 Loss를 제안한다.
먼전 간단하게 Cauchy-Schward inequality을 알아보면 다음과 같다.
$$|\overrightarrow{x} \cdot \overrightarrow{y}| \le \|\overrightarrow{x}\| \|\overrightarrow{y}\|$$
$$|\overrightarrow{x} \cdot \overrightarrow{y}| = \|\overrightarrow{x}\| \|\overrightarrow{y}\| \Leftrightarrow \overrightarrow{x} = c\overrightarrow{y}$$
두 벡터의 내적은 항상 두 백터의 곱보다 작거나 같다는 것 이다.
K-Means에 적용하면 다음과 같이 나타낼 수 있다.
$$D_{sc} = \frac{1}{k} \sum_{i=1}^{k-1} \sum_{j > i} \frac{\alpha_i^T K \alpha_j}{\sqrt{\alpha_i^T K \alpha_i \alpha_j^T K \alpha_j}}$$
- \(\alpha_1, \cdots, \alpha_k\): Column of hard cluster aiignment matrix \(A \in R^{n \times k}\)
위의 식을 생각하면 단순히, 하나의 sample이 여러 Cluster에 속하지 않게 학습하는 것으로서 생각할 수 있다.
해당 논문은 이러한 Hard한 Loss Funciton말고, softmax를 사용하여 다시 Loss를 정의한다.
$$D_{sim} = \frac{1}{k} \sum_{i=1}^{k-1} \sum_{j > i} \frac{\beta_i^T K \beta_j}{\sqrt{\beta_i^T K \beta_i \beta_j^T K \beta_j}}$$
- \(\beta_1, \cdots, \beta_k\): Column of \(B\)
- \(B = [\beta_{qi}] = exp(-\|\alpha_q - e_i\|)\)
- \(e_i\): ith corner of the simplex
식을 살펴보게 되면, 각각의 corner of the simplex위주로 Clustering되는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다. 하지만, corner of the simplex를 어떻게 Prior로 지정하는지, 혹은 Training중에 어떻게 지정하는지에 대해서는 나와있지 않습니다.
마지막으로 각각의 Column이 Orthogonal하게 하기 위하여 다음과 같은 Regularization을 추가하였습니다.
$$D_{reg} = triu(A^T A)$$
triu()은 upper traingular elements of its argument입니다.
최종적인 Cluster를 위한 Loss는 다음과 같습니다.
$$L_c = D_{sc} + D_{sim} + D_{reg}$$
Optimization Training
Training의 과정은 아래와 같습니다.
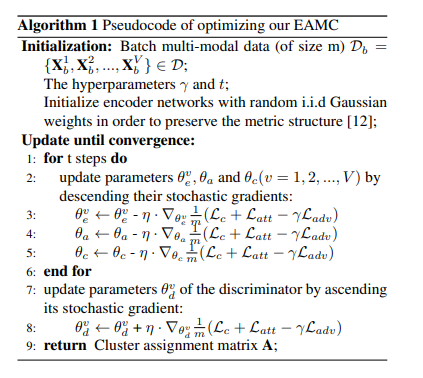
Experiment
많은 Experiment를 하였지만, 주요하게 살펴볼 결과는 크게 3가지 있다.
Compare to traditional Model: 기존의 Model보다 좋은 Performance를 보여주었다.
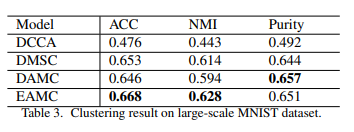
Impact of Network Architecture: Network구성요소에서 하나씩 제거하면서 결과를 살펴보았다. EX) \(\text{EAMC}_{adv}\)는 Network구성요소에서 Adversial Network를 제외한 결과이다. 결과를 살펴보게 되면, Adversial Network와 Attention Layer가 성능에 큰 영향을 미치는 것을 살펴볼 수 있다.
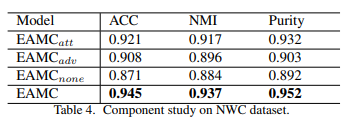
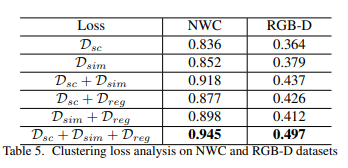
Impact of CLustering Loss: 3가지의 Clustering Loss의 모든 조합에 대해서 성능을 평가하였다. 각각의 모든 Loss를 사용하였을 때, 결과가 좋은 것을 알 수 있다.
Conclusion
해당 논문에서는 Multi-Modality를 Fusion및 End-to-End로서 학습할 수 있는 Model을 제안하였다. Adversial Network를 통하여 Modality를 Fusion하는 방식과, Attention Layer를 통하여 각 Modality의 중요도를 따로 학습하는 것이 현재 Paper에서 가장 큰 Contribution이라고 생각한다. 하지만, Code가 제공되지 않아서, Clustering Loss와 Network를 정확히 어떻게 구현했는지는 알 수 없었다.
참조: End-to-End Adversarial-Attention Network for Multi-Modal Clustering
코드에 문제가 있거나 궁금한 점이 있으면 wjddyd66@naver.com으로 Mail을 남겨주세요.

Leave a comment